Probiotic Combination CBLEB Alleviates Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Through Immune Regulation in Immunocompromised Rats
- PMID: 35210807
- PMCID: PMC8857997
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S348047
Probiotic Combination CBLEB Alleviates Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Through Immune Regulation in Immunocompromised Rats
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia, especially for people with immature or compromised immune systems. In addition to vaccination and antibiotics, immune regulation through microbial intervention has emerged in recent anti-SP infection research. This study investigated the therapeutic effect of a combination of live Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, and Bacillus (CBLEB), a widely used probiotic drug, on SP infection in rats.
Methods: An immunocompromised SP-infection rat model was established by intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide and nasal administration of SP strain ATCC49619. Samples from SP-infected, SP-infected and CBLEB-treated, and healthy rats were collected to determine blood indicators, serum cytokines, gut microbiota, faecal and serum metabolomes, lung- and colon-gene transcriptions, and histopathological features.
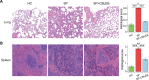
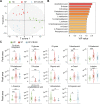
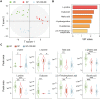
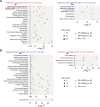
Results: CBLEB treatment alleviated weight loss, inflammation, organ damage, increase in basophil percentage, red cell distribution width, and RANTES levels and decrease in total protein and albumin levels of immunocompromised SP-infection rats. Furthermore, CBLEB treatment alleviated dysbiosis in gut microbiota, including altered microbial composition and the aberrant abundance of opportunistic pathogenic bacterial taxa such as Eggerthellaceae, and disorders in gut and serum metabolism, including altered metabolomic profiles and differentially enriched metabolites such as 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol in faeces and L-tyrosine in serum. The transcriptome analysis results indicated that the underlying mechanism by which CBLEB fights SP infection is mainly attributed to its regulation of immune-related pathways such as TLR and NLR signalling in the lungs and infection-, inflammation- or metabolism-related pathways such as TCR signalling in the colon.
Conclusion: The present study shows a potential value of CBLEB in the treatment of SP infection.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumonia infection; metabolism; microbiota; probiotics; transcriptome.
© 2022 Lv et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of the Immunomodulatory Effect of the Combination of Live Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, and Bacillus on Immunocompromised Rats.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;12:694344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.694344. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34211480 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus acidophilus LA14 Alleviates Liver Injury.mSystems. 2021 Jun 29;6(3):e0038421. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00384-21. Epub 2021 Jun 15. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34128694 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus sp. improved microbiota and metabolite profiles of aging rats.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Aug;146:104312. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104312. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31207344
-
Probiotics: use in allergic disorders: a Nutrition, Allergy, Mucosal Immunology, and Intestinal Microbiota (NAMI) Research Group Report.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Jul;42 Suppl 2:S91-6. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181639a98. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18542035 Review.
-
Immunology and probiotic impact of the newborn and young children intestinal microflora.Anaerobe. 2011 Dec;17(6):369-74. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Anaerobe. 2011. PMID: 21515397 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of glucose oxidase on growth performance, clinical symptoms, serum parameters, and intestinal health in piglets challenged by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 3;13:994151. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.994151. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36267185 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Treatment with Alcaligenes faecalis A12C Improves Host Resistance to Pathogens in Septic Rats: Possible Contribution of Curdlan-Like Immune Trainer.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Apr 26. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10252-0. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38668821
-
Endogenous Coriobacteriaceae enriched by a high-fat diet promotes colorectal tumorigenesis through the CPT1A-ERK axis.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Jan 20;10(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00472-7. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 38245554 Free PMC article.
-
Microcella aerolata GA224 exhibits preventive potential against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection via the gut-lung axis.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 9;41(7):259. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04478-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40632412
-
Roseicella aerolata GB24T from bioaerosol attenuates Streptococcus pneumoniae-introduced inflammation through regulation of gut microbiota and acetic acid.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1225548. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1225548. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37547684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO fact sheet on pneumonia provides key facts and information on causes, presenting features, economic costs, treatment, prevention and WHO response. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia. Accessed February 1, 2022.
-
- O’Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, et al. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet. 2009;374(9693):893–902. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

