Elevated ALCAM Expression Associated with Endotypes and Postoperative Recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
- PMID: 35210812
- PMCID: PMC8858028
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S350609
Elevated ALCAM Expression Associated with Endotypes and Postoperative Recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps (CRSwNP) is characterized by high heterogeneity and postoperative recurrence rate. This study aimed to explore the clinical significance of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM) in endotyping CRSwNP and predicting its recurrence.
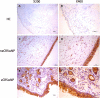
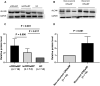
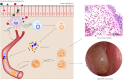
Methods: We recruited 120 CRSwNP patients including 70 non-eosinophilic CRSwNP (neCRSwNP) and 50 eosinophilic CRSwNP (eCRSwNP) patients, and 40 healthy controls (HCs). Serum and tissue samples were collected. Serum ALCAM levels were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and tissue ALCAM expression was assessed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting (WB) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The predictive values of ALCAM expression for CRSwNP endotypes and postoperative recurrence were assessed.
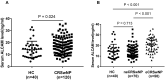
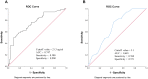
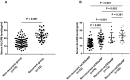
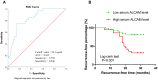
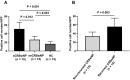
Results: The serum levels of ALCAM were significantly increased in CRSwNP patients in comparison with HCs and were correlated with the peripheral eosinophil count, tissue eosinophil counts, and percentage. Multivariate analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve highlighted that serum ALCAM levels were associated with CRSwNP endotypes. Tissue ALCAM expression was significantly enhanced in CRSwNP patients, especially in eCRSwNP patients. At the end of the study, 110 patients completed the follow-up schedule, 78 patients were categorized into the non-recurrent group, and the other 32 patients were included in the recurrent group. The serum ALCAM levels were elevated in the recurrent group compared with the non-recurrent group, and ALCAM expression in the tissue was significantly elevated. The ROC curve exhibited a high predictive ability of serum ALCAM in predicting postoperative recurrence. Logistic regression and Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrated that serum ALCAM was an independent risk factor for postoperative recurrence.
Conclusion: This is the first report suggesting that ALCAM expression was upregulated and associated with mucosal eosinophil infiltration and CRSwNP recurrence. Serum ALCAM could be a promising biomarker for distinguishing endotypes and predicting postoperative recurrence in CRwNP patients.
Keywords: activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; biomarker; chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; endotypes; recurrence.
© 2022 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in preparing this article.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

