Head on Comparison of Self- and Nano-assemblies of Gamma Peptide Nucleic Acid Amphiphiles
- PMID: 35210986
- PMCID: PMC8863176
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202109552
Head on Comparison of Self- and Nano-assemblies of Gamma Peptide Nucleic Acid Amphiphiles
Abstract
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) are nucleic acid analogs with superior hybridization properties and enzymatic stability than deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). In addition to gene targeting applications, PNAs have garnered significant attention as bio-polymer due to the Watson-Crick -based molecular recognition and flexibility of synthesis. Here, we engineered PNA amphiphiles using chemically modified gamma PNA (8 mer in length) containing hydrophilic diethylene glycol units at the gamma position and covalently conjugated lauric acid (C12) as a hydrophobic moiety. Gamma PNA (γPNA) amphiphiles self-assemble into spherical vesicles. Further, we formulate nano-assemblies using the amphiphilic γPNA as a polymer via ethanol injection-based protocols. We perform comprehensive head-on comparison of the physicochemical and cellular uptake properties of PNA derived self- and nano-assemblies. Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis reveal ellipsoidal morphology of γPNA nano-assemblies that results in superior cellular delivery compate to the spherical self-assembly. Next, we compare the functional activities of γPNA self-and nano-assemblies in lymphoma cells via multiple endpoints, including gene expression, cell viability, and apoptosis-based assays. Overall, we establish that γPNA amphiphile is a functionally active bio-polymer to formulate nano-assemblies for a wide range of biomedical applications.
Keywords: PNA amphiphiles; gamma peptide nucleic acids (γPNAs); micro-RNA-155; nano-assemblies; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

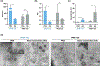



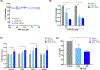
References
-
- Nielsen PE, Egholm M, Berg RH, Buchardt O, Science 1991, 254, 1497. - PubMed
-
- Wittung P, Nielsen PE, Buchardt O, Egholm M, Norden B, Nature 1994, 368, 561. - PubMed
-
- Demidov VV, Potaman VN, Frank-Kamenetskii MD, Egholm M, Buchard O, Sonnichsen SH, Nielsen PE, Biochem Pharmacol 1994, 48, 1310. - PubMed
-
- Egholm M, Buchardt O, Christensen L, Behrens C, Freier SM, Driver DA, Berg RH, Kim SK, Norden B, Nielsen PE, Nature 1993, 365, 566. - PubMed
-
- Bahal R, Ali McNeer N, Quijano E, Liu Y, Sulkowski P, Turchick A, Lu YC, Bhunia DC, Manna A, Greiner DL, Brehm MA, Cheng CJ, Lopez-Giraldez F, Ricciardi A, Beloor J, Krause DS, Kumar P, Gallagher PG, Braddock DT, Mark Saltzman W, Ly DH, Glazer PM, Nat Commun 2016, 7, 13304; - PMC - PubMed
- Bahal R, Quijano E, McNeer NA, Liu Y, Bhunia DC, Lopez-Giraldez F, Fields RJ, Saltzman WM, Ly DH, Glazer PM, Curr Gene Ther 2014, 14, 331; - PMC - PubMed
- Ricciardi AS, Bahal R, Farrelly JS, Quijano E, Bianchi AH, Luks VL, Putman R, Lopez-Giraldez F, Coskun S, Song E, Liu Y, Hsieh WC, Ly DH, Stitelman DH, Glazer PM, Saltzman WM, Nat Commun 2018, 9, 2481. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
