The Efficacy and Mid-term Durability of Urethral Sphincter Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
- PMID: 35211026
- PMCID: PMC8861290
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847520
The Efficacy and Mid-term Durability of Urethral Sphincter Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
Abstract
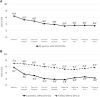
Aims: This study investigated the therapeutic effect of repeated urethral sphincter injections of autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in treatment of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in women due to intrinsic sphincter deficiency (ISD) refractory to medical treatment or after the first anti-incontinence surgery. Methods: Twenty-six women with SUI due to urodynamically proven ISD were prospectively enrolled. Five milliliters of PRP (2.5-5 times of the platelet concentrations in peripheral blood) were injected into the external sphincter at 5 sites, with 4 treatments at monthly interval. The primary end-point was post-treatment Global Response Assessment (GRA, scored 0-3) score after four PRP treatments. A GRA ≥ 2 was considered as a successful result. The secondary endpoints included changes in visual analog scale (VAS) of SUI and urodynamic parameters. The follow-up date was 12 months after the fourth PRP treatment. Results: The mean age was 61.7 ± 15.3 years. The overall success rate was 50% with the post-treatment mean GRA of 1.5 ± 1.1. Complete dryness was achieved in 12 patients (46.2%) after the PRP treatment, and 7 (26.9%) kept total continence at 12 months. The mean VAS of SUI score decreased significantly from 6.4 ± 2.3 to 3.9 ± 2.3 after treatment (p < 0.001). The abdominal leak point pressure increased significantly from 117.5 ± 63.8 to 133.6 ± 61.7 cmH2O (p = 0.045). No perioperative adverse events or severe complications occurred, except 1 (3.8%) patient reported straining to void which was self-limited. Conclusion: Repeated urethral sphincter injections of autologous PRP are a safe procedure that provides significant reduction in the severity of female SUI and a mid-term durability, suggesting PRP treatment is effective to increase urethral sphincter resistance for female SUI.
Keywords: female; patient reported outcome measures; stress urinary incontinence; urethra; urodynamics.
Copyright © 2022 Chiang and Kuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Efficacy and Mid-Term Durability of Urethral Sphincter Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections to Treat Postprostatectomy Stress Urinary Incontinence.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 8;10(9):2235. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092235. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140336 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Urethral Sphincter Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence due to Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency: A Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial.Int Neurourol J. 2021 Mar;25(1):51-58. doi: 10.5213/inj.2040272.136. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Int Neurourol J. 2021. PMID: 33504126 Free PMC article.
-
A novel management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence: platelet-rich plasma urethral sphincter injection.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 8;11(1):5371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84923-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33686126 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Intrinsic sphincter deficiency and female urinary incontinence].Prog Urol. 2015 Jun;25(8):437-54. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Prog Urol. 2015. PMID: 25864653 Review. French.
-
Stem cell applications in regenerative medicine for stress urinary incontinence: A review of effectiveness based on clinical trials.Arab J Urol. 2020 Apr 17;18(3):194-205. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2020.1750864. Arab J Urol. 2020. PMID: 33029431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PRP Therapy for Stress Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse: A New Frontier in Personalized Treatment?J Pers Med. 2025 May 22;15(6):214. doi: 10.3390/jpm15060214. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40559077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma for treatment of female stress urinary incontinence.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Feb;57(2):313-321. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04229-9. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39390198 Review.
-
The effect of injectable platelet rich fibrin as a nonsurgical treatment of the female stress urinary incontinence.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 May;309(5):2229-2236. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07431-3. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 38424182
-
Treating and Managing Urinary Incontinence: Evolving and Potential Multicomponent Medical and Lifestyle Interventions.Res Rep Urol. 2023 Jun 17;15:193-203. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S387205. eCollection 2023. Res Rep Urol. 2023. PMID: 37351339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regenerative Medicine in Urogynecology: Where We Are and Where We Want to Be.Urogynecology (Phila). 2024 May 1;30(5):519-527. doi: 10.1097/SPV.0000000000001461. Urogynecology (Phila). 2024. PMID: 38683203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M., Griffiths D., Rosier P., Ulmsten U., et al. (2002). The Standardisation of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn 21, 167–178. 10.1002/nau.10052 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M., Griffiths D., Rosier P., Ulmsten U., et al. (2003). The Standardisation of Terminology in Lower Urinary Tract Function: Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology 61, 37–49. 10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02243-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abrams P., Andersson K. E., Apostolidis A., Birder L., Bliss D., Brubaker L., et al. (2018). 6th International Consultation on Incontinence. Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: EVALUATION and TREATMENT of URINARY INCONTINENCE, PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE and FAECAL INCONTINENCE. Neurourol Urodyn 37, 2271–2272. 10.1002/nau.23551 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Agarwal B. K., Agarwal N. (2017). Urinary Incontinence: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Impact on Quality of Life and Treatment Seeking Behaviour Among Middle Aged Women. Int. Surg. J. 4, 1953–1958. 10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172131 - DOI
-
- Alessio-Mazzola M., Lovisolo S., Sonzogni B., Capello A. G., Repetto I., Formica M., et al. (2021). Clinical Outcome and Risk Factor Predictive for Failure of Autologous PRP Injections for Low-To-Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. (Hong Kong) 29, 230949902110219. 10.1177/23094990211021922 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

