Psychological and Emotional Recognition of Preschool Children Using Artificial Neural Network
- PMID: 35211052
- PMCID: PMC8861073
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.762396
Psychological and Emotional Recognition of Preschool Children Using Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
The artificial neural network (ANN) is employed to study children's psychological emotion recognition to fully reflect the psychological status of preschool children and promote the healthy growth of preschool children. Specifically, the ANN model is used to construct the human physiological signal measurement platform and emotion recognition platform to measure the human physiological signals in different psychological and emotional states. Finally, the parameter values are analyzed on the emotion recognition platform to identify the children's psychological and emotional states accurately. The experimental results demonstrate that the recognition ability of children aged 4-6 to recognize the three basic emotions of happiness, calm, and fear increases with age. Besides, there are significant age differences in children's recognition of happiness, calm, and fear. In addition, the effect of 4-year-old children on the theory of mind tasks is less than that of 5- to 6-year-old children, which may be related to more complex cognitive processes. Preschool children are experiencing a stage of rapid emotional development. If children cannot be guided to reasonably identify and deal with emotions at this stage, their education level and social ability development will be significantly affected. Therefore, this study has significant reference value for preschool children's emotional recognition and guidance and can promote children's emotional processing and mental health.
Keywords: artificial neural network; education; emotion recognition; preschool children; traditional education.
Copyright © 2022 Rao, Wu, Zhang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
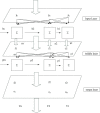
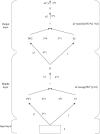
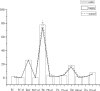
Figures








Similar articles
-
Age-related changes in emotion recognition across childhood: A meta-analytic review.Psychol Bull. 2024 Sep;150(9):1094-1117. doi: 10.1037/bul0000442. Psychol Bull. 2024. PMID: 39298231 Review.
-
Associations between vocal emotion recognition and socio-emotional adjustment in children.R Soc Open Sci. 2021 Nov 17;8(11):211412. doi: 10.1098/rsos.211412. eCollection 2021 Nov. R Soc Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 34804582 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of young children's self-reports of their emotion in response to structured laboratory tasks.Emotion. 2010 Aug;10(4):519-35. doi: 10.1037/a0019008. Emotion. 2010. PMID: 20677869
-
Recognition of children's emotional facial expressions among mothers reporting a history of childhood maltreatment.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 29;15(12):e0243083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243083. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33373377 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental origins of naïve psychology in infancy.Adv Child Dev Behav. 2009;37:55-104. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2407(09)03702-1. Adv Child Dev Behav. 2009. PMID: 19673160 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Neural Networks for Short-Form Development of Psychometric Tests: A Study on Synthetic Populations Using Autoencoders.Educ Psychol Meas. 2024 Feb;84(1):62-90. doi: 10.1177/00131644231164363. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Educ Psychol Meas. 2024. PMID: 38250505 Free PMC article.
-
An Intelligent Mental Health Identification Method for College Students: A Mixed-Method Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 14;19(22):14976. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214976. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429697 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional and Behavioral Changes in Preschool Firstborn Children During Transition to Siblinghood: A Mixed Methods Study.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023 Jun 3;16:2029-2044. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S411729. eCollection 2023. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023. PMID: 37292056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahareh N., Mohammad N., Andry R. (2018). Long short-term memory hyperparameter optimization for a neural network based emotion recognition framework. IEEE Access 6 49325–49338. 10.1109/access.2018.2868361 - DOI
-
- Bao Y. L. (2021). On early identification and Countermeasures of children’s emotional problems. Chin. Teach. 26 81–82.
-
- Batbaatar E., Li M., Ryu H. (2019). Semantic-Emotion Neural Network for Emotion Recognition from Text. IEEE Access 49 839–847.
-
- Chen L. F., Zhou M., Su W. J., Wu M., She J., Hirota K. (2018). Softmax regression based deep sparse autoencoder network for facial emotion recognition in human-robot interaction. Inf. Sci. 428 49–61. 10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.044 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

