Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 35211110
- PMCID: PMC8861075
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.768560
Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
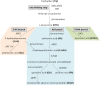
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Several risk factors including unhealthy lifestyle, genetic background, obesity, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, smoking, age, etc. contribute to the development of coronary atherosclerosis and subsequent coronary artery disease. Inflammation plays an important role in coronary artery disease development and progression. Pro-inflammatory signals promote the degradation of tryptophan via the kynurenine pathway resulting in the formation of several immunomodulatory metabolites. An unbalanced kynurenic pathway has been implicated in the pathomechanisms of various diseases including CAD. Significant improvements in detection methods in the last decades may allow simultaneous measurement of multiple metabolites of the kynurenine pathway and such a thorough analysis of the kynurenine pathway may be a valuable tool for risk stratification and determination of CAD prognosis. Nevertheless, imbalance in the activities of different branches of the kynurenine pathway may require careful interpretation. In this review, we aim to summarize clinical evidence supporting a possible use of kynurenine pathway metabolites as clinical biomarkers in various manifestations of CAD.
Keywords: IDO activity/detection; ischemic heart disease; kynurenic acid; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; personalized medicine; prediction; tryptophan.
Copyright © 2022 Gáspár, Halmi, Demján, Berkecz, Pipicz and Csont.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Steenbergen C, Frangogiannis NG. Chapter 36 - Ischemic Heart Disease. In: Hill JA, Olson EN, editors. Muscle. Boston/Waltham: Academic Press; (2012). p. 495–521.
-
- Knuuti J. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Coronary Syndromes The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Coronary Syndromes of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Russ J Cardiol (2020) 25(2):119–80. doi: 10.15829/1560-4071-2020-2-3757 - DOI
-
- Collet J-P, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, et al. . 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation: The Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J (2021) 42(14):1289–367. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

