The Recombinant E g.P29-Mediated miR-126a-5p Promotes the Differentiation of Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cells via DLK1-Mediated Notch1 Signal Pathway
- PMID: 35211114
- PMCID: PMC8861942
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.773276
The Recombinant E g.P29-Mediated miR-126a-5p Promotes the Differentiation of Mouse Naive CD4+ T Cells via DLK1-Mediated Notch1 Signal Pathway
Abstract
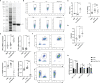
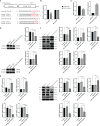
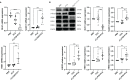
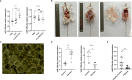
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a zoonotic parasitic disease spread worldwide caused by Echinococcus granulosus (Eg), which sometimes causes serious damage; however, in many cases, people are not aware that they are infected. A number of recombinant vaccines based on Eg are used to evaluate their effectiveness against the infection. Our previous report showed that recombinant Eg.P29 (rEg.P29) has a marvelous immunoprotection and can induce Th1 immune response. Furthermore, data of miRNA microarray in mice spleen CD4+ T cells showed that miR-126a-5p was significantly elevated 1 week after immunization by using rEg.P29. Therefore, in this perspective, we discussed the role of miR-126a-5p in the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into Th1/Th2 under rEg.P29 immunization and determined the mechanisms associated with delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) and Notch1 signaling pathway. One week after P29 immunization of mice, we found that miR-126a-5p was significantly increased and DLK1 expression was decreased, while Notch1 pathway activation was enhanced and Th1 response was significantly stronger. The identical conclusion was obtained by overexpression of mmu-miR-126a-5p in primary naive CD4+ T cells in mice. Intriguingly, mmu-miR-126a-5p was significantly raised in serum from mice infected with protoscolex in the early stages of infection and markedly declined in the late stages of infection, while has-miR-126-5p expression was dramatically reduced in serum from CE patients. Taken together, we show that miR-126a-5p functions as a positive regulator of Notch1-mediated differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th1 through downregulating DLK1 in vivo and in vitro. Hsa-miR-126-5p is potentially a very promising diagnostic biomarker for CE.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; Cystic Echinococcocosis; DLK1; Notch1; Th1; Th2; miR-126a-5p; rEg.P29.
Copyright © 2022 Du, Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Tao, Yang, Zhu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

