Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Safety of Shuxuening Injection in the Treatment of Unstable Angina
- PMID: 35211180
- PMCID: PMC8863456
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6650763
Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Safety of Shuxuening Injection in the Treatment of Unstable Angina
Abstract
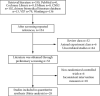
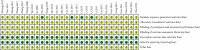
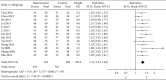
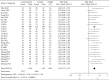
The aim of this study was to systematically review the efficacy and safety of Shuxuening injection combined with conventional Western medicine in the treatment of unstable angina. Randomized controlled trials of Shuxuening injection combined with conventional Western medicine in the treatment of unstable angina were searched by the computer system from PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, VIP, CNKI, Wanfang Database, and Chinese Biomedical Database since the establishment of the database until June 2020, according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the selection of literature, using Rev Man5.3 Meta-analysis Software. The 28 randomized controlled trials were included, with a total of 3,127 patients. Meta-analysis results showed that Shuxuening injection combined with conventional western medicine was effective in improving the clinical efficacy of angina pectoris (RR = 1.23, 95% CI [1.19, 1.27], P<0.00001), improvement of ECG (RR = 1.31, 95% CI [1.23, 1.40], P < 0.00001), reduction of angina pectoris attack frequency (MD = -1.28, 95% CI [-1.88, -0.67], P < 0.0001), duration of angina (MD = -3.36, 95% CI [-3.69, -3.03], P < 0.00001), nitroglycerin dosage (MD = -0.39, 95% CI [-0.65, -0.13], P = 0.003), C-reactive protein (MD = -2.72, 95% CI [-3.41, -2.03], P < 0.00001), BNP (MD = -23.33, 95% CI [-27.87, -18.79], P < 0.00001), lower triglycerides (MD = -0.72, 95% CI [-1.05, -0.38], P < 0.0001), total cholesterol (MD = -1.39, 95% CI [-1.84, -0.94], P < 0.00001), and LDL cholesterol (MD = -1.20, 95% CI [-2.12, -0.29], P = 0.01) which is better than that of control group. The effect on raising HDL cholesterol was comparable between the two groups (MD = 0.49, 95% CI [-0.06, 1.04], P = 0.08) and the incidence of adverse reactions to differences had no statistical significance (RR = 0.99, 95% CI [0.54, 1.81], P = 0.97). The Shuxuening injection combined with conventional Western medicine in the treatment of unstable angina has clear efficacy and a certain degree of safety, so it is recommended for clinical application.
Copyright © 2022 Genhao Fan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Systematic Evaluation of Clinical Efficacy and Platelet Function of Sofren Injection in the Treatment of Angina Pectoris.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 26;2021:5591137. doi: 10.1155/2021/5591137. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33854555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of Xueshuantong (lyophilized) for injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 7;14:1074400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1074400. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089918 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy of Puerarin Injection as Adjunctive Therapy for Unstable Angina Pectoris.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 24;9:763567. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.763567. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35282378 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 31;18(8):e0290841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290841. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37651454 Free PMC article.
-
[Effictiveness and safety of Xueshuantong Injection in treatment of unstable angina pectoris: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Oct;44(20):4366-4378. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190724.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31872621 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Shuxuening injection in coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 18;14:1265603. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265603. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37790809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and safety of selected traditional Chinese medicine injections in patients with combined diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1060956. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1060956. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36699083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shen Y., He G., Xiao T., Yu L. New progress in the diagnosis and treatment of unstable angina. Popular Science and Technology . 2019;21(11):51–53.
-
- Hu S. Clinical application and safe use of Shuxuening injection. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine . 2012;32(11):78–81.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

