Membranous nephropathy associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease successfully treated with obinutuzumab
- PMID: 35211311
- PMCID: PMC8862033
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfab250
Membranous nephropathy associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease successfully treated with obinutuzumab
Abstract
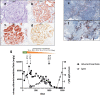
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-releated disease is typically associated with interstitial nephritis, but rare cases of idiopathic membranous nephropathy as a renal manifestation have been described. Obinutuzumab was successfully used in refractory membranous nephropathy, but evidence for the treatment of IgG4-related disease with obinutuzumab is lacking. We report one patient's case with membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease who was treated with obinutuzumab following an anaphylactic reaction to rituximab. Obinutuzumab treatment resulted in a sustained complete remission of membranous nephropathy and a decrease of IgG4 to the normal range. This case demonstrates that membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease can be treated successfully with obinutuzumab.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; IgG4-related disease; kidney disease; membranous nephropathy.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
Comment in
-
B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease.Eur J Intern Med. 2023 Oct;116:155-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2023.07.019. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Eur J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37481424 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari Set al. . The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79: 77–87 - PubMed
-
- Cravedi P, Abbate M, Gagliardini Eet al. . Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease. Am J Kidney Dis 2011; 58: 272–275 - PubMed
-
- Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi Aet al. . Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74: 1171–1177 - PubMed
-
- Klomjit N, Fervenza FC, Zand L. Successful treatment of patients with refractory PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy with obinutuzumab: a report of 3 cases. Am J Kidney Dis 2020; 76: 883–888 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

