Combination of Venetoclax and Midostaurin Efficiently Suppressed Relapsed t(8;21)Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Mutant KIT After Failure of Venetoclax Plus Azacitidine Treatment
- PMID: 35211416
- PMCID: PMC8861361
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.841276
Combination of Venetoclax and Midostaurin Efficiently Suppressed Relapsed t(8;21)Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Mutant KIT After Failure of Venetoclax Plus Azacitidine Treatment
Abstract
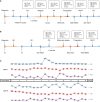
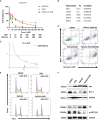
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with t(8;21) is categorized as favorable-risk AML, but KIT mutations show a significantly poor prognostic impact in such patients. Persistent vulnerability to relapse is a major challenge in the treatment of this subtype of patients. Venetoclax is a BCL-2 selective inhibitor. The venetoclax+HMA strategy is also a notable salvage regimen that achieves good clinical outcomes in the treatment of relapsed or refractory (R/R) AML. However, in our clinical practice, we found that disease progressed rapidly even after venetoclax+azacitidine (AZA) therapy in two relapsed t(8;21) AML patients with KIT mutations. We report for the first time the therapeutic potential of venetoclax+midostaurin as a new combination therapy for relapsed t(8;21) AMLs with KIT mutations showing resistance to venetoclax+AZA therapy. Our ex vivo study also showed that midostaurin alone could inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of Kasumi-1 cells (e.g. Midostaurin induced G2 phase cell arrest, down-regulated p-KIT and BCL-2, while Bax protein levels were up-regulated) and observed a synergistic anti effect when the two drugs were combined. Our study shows that the venetoclax+midostaurin regimen may be a promising treatment option for R/R t(8;21) AML with KIT mutations.
Keywords: KIT mutation; azacitidine; midostaurin; relapsed acute myeloid leukemia; t(8;21); targeted therapy; venetoclax.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Wang, Ge, Qiu, Du, Shan, Shen, Wan, Wang, Wu, Qiu and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Marcucci G, Mrozek K, Ruppert AS, Maharry K, Kolitz JE, Moore JO, et al. . Prognostic Factors and Outcome of Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients With T(8;21) Differ From Those of Patients With Inv(16): A Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study. J Clin Oncol (2005) 23:5705–17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.15.610 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

