Sequential sagittal alignment changes in the cervical spine after occipitocervical fusion
- PMID: 35211550
- PMCID: PMC8855180
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1172
Sequential sagittal alignment changes in the cervical spine after occipitocervical fusion
Abstract
Background: There are few studies regarding sequential changes in the sagittal alignment of the upper and lower cervical regions of the spine after occipitocervical fusion (OCF). In addition, no comparisons of cervical sagittal alignment (CSA) between patients with craniocervical junction disorders (CJDs) and normal populations have been reported.
Aim: To compare the CSA of patients with CJDs with that of normal controls and investigate the sequential changes in the CSA of the upper and lower cervical spine after OCF.
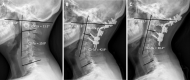
Methods: Eighty-four patients who underwent OCF (OCF group) and 42 asymptomatic volunteers (control group) were included. Radiographic parameters, including the occipital to C2 angle (O-C2a), occipital and external acoustic meatus to axis angle (O-EAa), C2-7 angle (C2-7a), and pharyngeal inlet angle (PIA), were measured and compared pre- and postoperatively. The correlations among the parameters were analyzed using Pearson's correlation test.
Results: The O-C2a and PIA of the OCF group were smaller than those of the control group, while their O-EAa and C2-7a values were larger than those of the normal controls. There were no significant differences in O-C2a, C2-7a, or PIA in the OCF group at baseline, 1 mo, or the final follow-up after surgery. The Pearson's correlation results showed that there were significant correlations between the O-C2a and C2Ta, C2-7a, C2-7 sagittal vertical axis (SVA), and PIA at 1 mo after OCF surgery and between O-C2a and O-EAa, C2Ta, C2-7a, C2-7 SVA, and PIA at the final follow-up.
Conclusion: Patients with CJDs have a more kyphotic upper CSA and a more lordotic lower CSA than normal controls. The effectiveness of OCF surgery in restoring CSA may be limited by the realignment of the craniocervical junction being neglected. The reduction in O-C2a after OCF surgery may increase C2-7a and decrease PIA.
Keywords: Cervical spine; Craniocervical disorders; Dysphagia; Occipitocervical fusion; Sagittal alignment.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Nojiri K, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Maruiwa H, Nakamura M, Nishizawa T, Toyama Y. Relationship between alignment of upper and lower cervical spine in asymptomatic individuals. J Neurosurg. 2003;99:80–83. - PubMed
-
- Patwardhan AG, Khayatzadeh S, Havey RM, Voronov LI, Smith ZA, Kalmanson O, Ghanayem AJ, Sears W. Cervical sagittal balance: a biomechanical perspective can help clinical practice. Eur Spine J. 2018;27:25–38. - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Kim KT, Seo EM, Suk KS, Kwack YH, Son ES. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25:E41–E47. - PubMed
-
- Huang JC, Qian BP, Qiu Y, Yu Y, Ni HB. Surgical overreduction and hyperlordotic fusion of C1-C2 joint are associated with cervical sagittal malalignment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137:1631–1639. - PubMed
-
- Kim JT, Lee HJ, Choi DY, Shin MH, Hong JT. Sequential alignment change of the cervical spine after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion in the lower cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:2223–2232. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

