Unusual magnetic resonance imaging findings of brain and leptomeningeal metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma: A case report
- PMID: 35211615
- PMCID: PMC8855273
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1723
Unusual magnetic resonance imaging findings of brain and leptomeningeal metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma: A case report
Abstract
Background: Metastatic tumors are the most common malignancies of central nervous system in adults, and the frequent primary lesion is lung cancer. Brain and leptomeningeal metastases are more common in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. However, the coexist of brain metastasis with leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) in isolated gyriform appearance is rare.
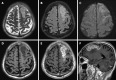
Case summary: We herein presented a case of a 76-year-old male with an established diagnosis as lung adenocarcinoma with gyriform-appeared cerebral parenchymal and leptomeningeal metastases, accompanied by mild peripheral edema and avid contrast enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging. Surgical and pathological examinations confirmed the brain and leptomeningeal metastatic lesions in the left frontal cortex, subcortical white matter and local leptomeninges.
Conclusion: This case was unique with respect to the imaging findings of focal gyriform appearance, which might be caused by secondary parenchymal brain metastatic tumors invading into the leptomeninges or coexistence with LM. Radiologists should be aware of this uncommon imaging presentation of tumor metastases to the central nervous system.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Case report; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Leptomeningeal metastasis; Lung cancer; Magnetic resonance imaging.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment of Leptomeningeal Metastases in a Patient with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR T790M Mutation.Case Rep Oncol. 2017 Sep 20;10(3):840-845. doi: 10.1159/000480452. eCollection 2017 Sep-Dec. Case Rep Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29070999 Free PMC article.
-
Solitary Leptomeningeal Metastasis from Lung Cancer: A Case Report.NMC Case Rep J. 2022 Sep 23;9:323-328. doi: 10.2176/jns-nmc.2022-0113. eCollection 2022. NMC Case Rep J. 2022. PMID: 36313794 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Treatment With Afatinib of Lung Adenocarcinoma With Leptomeningeal Metastasis Harboring the Exon 18 p.G719A Mutation in the EGFR Gene Was Detected in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Case Report.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 8;10:1635. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01635. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014823 Free PMC article.
-
The Underlying Biology and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities of Leptomeningeal Metastases in Adult Solid Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 10;13(4):732. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040732. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33578853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FLAIR hyperintensity along the brainstem surface in leptomeningeal metastases: a case series and literature review.Cancer Imaging. 2020 Nov 23;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00361-8. Cancer Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33228799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2865–2872. - PubMed
-
- Ostrom QT, Wright CH, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. Brain metastases: epidemiology. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;149:27–42. - PubMed
-
- Remon J, Le Rhun E, Besse B. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A continuing challenge in the personalized treatment era. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;53:128–137. - PubMed
-
- Li YS, Jiang BY, Yang JJ, Tu HY, Zhou Q, Guo WB, Yan HH, Wu YL. Leptomeningeal Metastases in Patients with NSCLC with EGFR Mutations. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1962–1969. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

