Efficacy and Safety of Roluperidone for the Treatment of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
- PMID: 35211743
- PMCID: PMC9077422
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbac013
Efficacy and Safety of Roluperidone for the Treatment of Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: This is a placebo-controlled multi-national trial of roluperidone, a compound with antagonist properties for 5-HT2A, sigma2, and α1A-adrenergic receptors, targeting negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. This trial follows a previous trial that demonstrated roluperidone superiority over placebo in a similar patient population.
Methods: Roluperidone 32 mg/day, roluperidone 64 mg/day, or placebo was administered for 12 weeks to 513 patients with schizophrenia with moderate to severe negative symptoms. The primary endpoint was the PANSS-derived Negative Symptom Factor Score (NSFS) and the key secondary endpoint was Personal and Social Performance scale (PSP) total score.
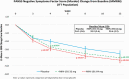
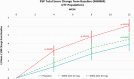
Results: NSFS scores were lower (improved) for roluperidone 64 mg compared to placebo and marginally missing statistical significance for the intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis data set (P ≤ .064), but reached nominal significance (P ≤ .044) for the modified-ITT (m-ITT) data set. Changes in PSP total score were statistically significantly better on roluperidone 64 mg compared to placebo for both ITT and m-ITT (P ≤ .021 and P ≤ .017, respectively).
Conclusions: Results of this trial confirm the potential of roluperidone as a treatment of negative symptoms and improving everyday functioning in patients with schizophrenia. Study registration: Eudra-CT: 2017-003333-29; NCT03397134.
Keywords: negative symptoms; schizophrenia; treatment.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Figures
References
-
- Galderisi S, Mucci A, Buchanan RW, Arango C. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia: new developments and unanswered research questions. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:664–677. - PubMed
-
- Szczypiński JJ, Gola M. Dopamine dysregulation hypothesis: the common basis for motivational anhedonia in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia? Rev Neurosci. 2018;29:727–744. - PubMed
-
- Millan MJ, Fone K, Steckler T, Horan WP. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia: clinical characteristics, pathophysiological substrates, experimental models and prospects for improved treatment. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;24:645–692. - PubMed
-
- Kirkpatrick B. Developing concepts in negative symptoms: primary vs secondary and apathy vs expression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2014;75:30–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous