Personalized tourniquet pressure may be a better choice than uniform tourniquet pressure during total knee arthroplasty: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
- PMID: 35212310
- PMCID: PMC8878703
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028981
Personalized tourniquet pressure may be a better choice than uniform tourniquet pressure during total knee arthroplasty: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Pneumatic tourniquets are widely used in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Some surgeons prefer a uniform tourniquet inflation pressure (UTIP) for all patients; others use personalized tourniquet inflation pressures (PTIP) based on systolic blood pressure and limb occlusion pressure. However, no consensus exists regarding the optimal mode of inflation pressure during TKA. This review aimed to appraise if personalized tourniquet inflation pressures are better than uniform tourniquet inflation.
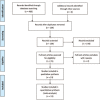
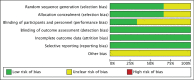
Methods: The databases (Web of Science, Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, Cochrane Library, Highwire, CBM, CNKI, VIP, Wanfang) were searched on March 2021 to systematically identify and screen the literature for randomized controlled trials involving PTIP and UTIP during total knee arthroplasty.
Results: Thirteen randomized controlled trials, involving 1204 TKAs (1201 patients) were included in the systematic review. The meta-analysis identified a trend toward less visual analogue scale (VAS) score at rest with PTIP group at 1 day (P = .002), 2 to 3 days (P = .01), and less VAS score at activity 1 day (P < .0001), 2 to 3 days after the operation (P < .00001), and discharge (P < .0001). No significant difference was found between the groups in terms of VAS score at rest when discharge (P = 1.0). We also found no significant difference in terms of intraoperative blood loss (P = .48), total blood loss (P = .15), lower limb vein thrombosis (P = .42), and thigh bullae (P = .17). However, in the PTIP group, we found a significant higher hospital for special surgery (HSS) score (P = .007), broader knee Range of motion (P = .02), less rate of thigh ecchymosis (P = .00001), and shorter thigh circumference at 1 day (P = .006), 2 to 3 days (P = .0005), and discharge (P = .02).
Conclusion: PTIP provides a similar bloodless surgical field compared with the conventional UTIP. Furthermore, PTIP provides less pain intensity, thigh circumference, rate of thigh ecchymosis, higher hospital for special surgery, and better initial recovery of knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Therefore, we recommend using a PTIP method during TKA. More adequately powered and better-designed randomized controlled trials studies with long-term follow-up are required to produce evidence-based guidelines regarding the PTIP method.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

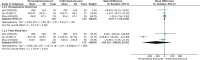


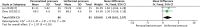

Similar articles
-
Personalized tourniquet pressure versus uniform tourniquet pressure in trauma orthopedic surgery of extremities: a prospective randomized controlled study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):721. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05217-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39497107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty when tranexamic acid was used: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jan 15;17(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02898-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35033124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Tourniquet Use in TKA Increase Postoperative Pain? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Mar;477(3):547-558. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000572. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 30461513 Free PMC article.
-
More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Jun;28(6):1842-1860. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05617-w. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 31289914
-
Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss, pain, functional recovery, and complications in robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized controlled trial.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 21;17(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02992-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35189911 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of tourniquet use in paediatric orthopaedic surgery: can we extrapolate from adult guidelines?EFORT Open Rev. 2024 Jan 9;9(1):80-91. doi: 10.1530/EOR-23-0091. EFORT Open Rev. 2024. PMID: 38193578 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty is not associated with increased risk of postoperative deep vein thrombosis.J Exp Orthop. 2023 Jun 29;10(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40634-023-00628-6. J Exp Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37382867 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of orthopedic operating room personnel regarding the use of pneumatic tourniquets.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 24;19(7):e0307545. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307545. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 Jun 3;20(6):e0325629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325629. PMID: 39047025 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Personalized tourniquet pressure versus uniform tourniquet pressure in trauma orthopedic surgery of extremities: a prospective randomized controlled study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Nov 5;19(1):721. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05217-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39497107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can We Forgo the Use of Tourniquets in Total Knee Arthroplasty?Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2024 Apr 10;59(2):e235-e240. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1785204. eCollection 2024 Apr. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 38606140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noordin S, McEwen JA, Kragh JF, Jr, Eisen A, Masri BA. Surgical tourniquets in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91:2958–67. - PubMed
-
- Odinsson A, Finsen V. Tourniquet use and its complications in Norway. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88:1090–2. - PubMed
-
- Olivecrona C, Ponzer S, Hamberg P, Blomfeldt R. Lower tourniquet cuff pressure reduces postoperative wound complications after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study of 164 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2012;94:2216–21. - PubMed
-
- Berry DJ, Bozic KJ. Current practice patterns in primary hip and knee arthroplasty among members of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons. J Arthroplasty 2010;25: (6 suppl): 02–4. - PubMed

