Deletion of Slc6a14 reduces cancer growth and metastatic spread and improves survival in KPC mouse model of spontaneous pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 35212370
- PMCID: PMC9022989
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20210855
Deletion of Slc6a14 reduces cancer growth and metastatic spread and improves survival in KPC mouse model of spontaneous pancreatic cancer
Abstract
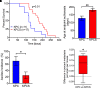
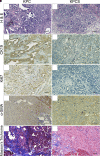
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is lethal. There is a dire need for better therapeutic targets. Cancer cells have increased demand for sugars, amino acids, and lipids and therefore up-regulate various nutrient transporters to meet this demand. In PDAC, SLC6A14 (an amino acid transporter (AAT)) is up-regulated, affecting overall patient survival. Previously we have shown using in vitro cell culture models and in vivo xenograft mouse models that pharmacological inhibition of SLC6A14 with α-methyl-l-tryptophan (α-MLT) attenuates PDAC growth. Mechanistically, blockade of SLC6A14-mediated amino acid transport with α-MLT leads to amino acid deprivation, eventually inhibiting mTORC1 signaling pathway, in tumor cells. Here, we report on the effect of Slc6a14 deletion on various parameters of PDAC in KPC mice, a model for spontaneous PDAC. Pancreatic tumors in KPC mice show evidence of Slc6a14 up-regulation. Deletion of Slc6a14 in this mouse attenuates PDAC growth, decreases the metastatic spread of the tumor, reduces ascites fluid accumulation, and improves overall survival. At the molecular level, we show lower proliferation index and reduced desmoplastic reaction following Slc6a14 deletion. Furthermore, we find that deletion of Slc6a14 does not lead to compensatory up-regulation in any of the other amino transporters. In fact, some of the AATs are actually down-regulated in response to Slc6a14 deletion, most likely related to altered mTORC1 signaling. Taken together, these results underscore the positive role SLC6A14 plays in PDAC growth and metastasis. Therefore, SLC6A14 is a viable drug target for the treatment of PDAC and also for any other cancer that overexpresses this transporter.
Keywords: KPC; SLC6A14; ascites fluid; metastasis; pancreatic cancer; survival.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Amino acid transporter SLC38A5 is a tumor promoter and a novel therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 6;13(1):16863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43983-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37803043 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid transporter SLC6A14 is a novel and effective drug target for pancreatic cancer.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;173(23):3292-3306. doi: 10.1111/bph.13616. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27747870 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the amino acid transporter Slc6a14 suppresses tumour growth in spontaneous mouse models of breast cancer.Biochem J. 2015 Jul 1;469(1):17-23. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150437. Epub 2015 May 13. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26173258
-
SLC6A14, a Na+/Cl--coupled amino acid transporter, functions as a tumor promoter in colon and is a target for Wnt signaling.Biochem J. 2020 Apr 30;477(8):1409-1425. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200099. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32219372 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Transporter SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) - A Target in Combined Anti-cancer Therapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 21;8:594464. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.594464. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
α-methyltryptophan-mediated protection against diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice as studied with a metabolomics approach.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 20;15:1463673. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1463673. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39902076 Free PMC article.
-
Reshaping the Binding Pocket of the Neurotransmitter:Solute Symporter (NSS) Family Transporter SLC6A14 (ATB0,+) Selectively Reduces Access for Cationic Amino Acids and Derivatives.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 1;12(10):1404. doi: 10.3390/biom12101404. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291613 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting the Achilles' heel of cancer: disrupting glutamine metabolism for effective cancer treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1345522. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1345522. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38510646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic profiling of solute carriers characterizes serine transport in cancer.Nat Metab. 2023 Dec;5(12):2148-2168. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00936-2. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 38066114 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid transporter SLC38A5 is a tumor promoter and a novel therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 6;13(1):16863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43983-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37803043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahib, L., Smith, B.D., Aizenberg, R., Rosenzweig, A.B., Fleshman, J.M. and Matrisian, L.M. (2014) Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74, 2913–2921 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

