Attention module improves both performance and interpretability of four-dimensional functional magnetic resonance imaging decoding neural network
- PMID: 35212436
- PMCID: PMC9057093
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25813
Attention module improves both performance and interpretability of four-dimensional functional magnetic resonance imaging decoding neural network
Abstract
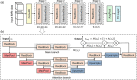
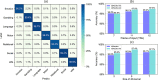
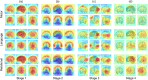
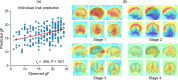
Decoding brain cognitive states from neuroimaging signals is an important topic in neuroscience. In recent years, deep neural networks (DNNs) have been recruited for multiple brain state decoding and achieved good performance. However, the open question of how to interpret the DNN black box remains unanswered. Capitalizing on advances in machine learning, we integrated attention modules into brain decoders to facilitate an in-depth interpretation of DNN channels. A four-dimensional (4D) convolution operation was also included to extract temporo-spatial interaction within the fMRI signal. The experiments showed that the proposed model obtains a very high accuracy (97.4%) and outperforms previous researches on the seven different task benchmarks from the Human Connectome Project (HCP) dataset. The visualization analysis further illustrated the hierarchical emergence of task-specific masks with depth. Finally, the model was retrained to regress individual traits within the HCP and to classify viewing images from the BOLD5000 dataset, respectively. Transfer learning also achieves good performance. Further visualization analysis shows that, after transfer learning, low-level attention masks remained similar to the source domain, whereas high-level attention masks changed adaptively. In conclusion, the proposed 4D model with attention module performed well and facilitated interpretation of DNNs, which is helpful for subsequent research.
Keywords: attention module; brain decoding; deep learning; functional magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimaging.
© 2022 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Clark, D. , & Badea, C. (2019). Convolutional regularization methods for 4D, x‐ray CT reconstruction. Medical Imaging 2019: Physics of Medical Imaging. Proceedings of SPIE, San Diego, CA. 10948, 574–585. 10.1117/12.2512816 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

