Effect of lanthanum carbonate on serum calciprotein particles in patients with stage 3-4 CKD-results from a placebo-controlled randomized trial
- PMID: 35212735
- PMCID: PMC9923701
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfac043
Effect of lanthanum carbonate on serum calciprotein particles in patients with stage 3-4 CKD-results from a placebo-controlled randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Calciprotein particles (CPP) are colloidal aggregates of calcium phosphate and the mineral-binding protein fetuin-A, and are potential mediators of cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Emerging evidence suggests non-calcium-containing phosphate binders may reduce serum CPP in patients with kidney failure who require dialysis; however, it is unclear whether similar interventions are effective in patients with earlier stages of CKD.
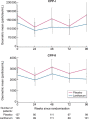
Methods: The IMpact of Phosphate Reduction On Vascular End-points in CKD (IMPROVE-CKD) was a multi-centre, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of lanthanum carbonate on cardiovascular markers in 278 participants with stage 3b/4 CKD. In this pre-specified exploratory analysis, primary (CPP-I) and secondary CPP (CPP-II) were measured in a sub-cohort of participants over 96 weeks. Treatment groups were compared using linear mixed-effects models and the relationship between serum CPP and pulse wave velocity (PWV) and abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) was examined.
Results: A total of 253 participants had CPP data for baseline and at least one follow-up timepoint and were included in this analysis. The mean age was 62.4 ± 12.6 years, 32.0% were female and the mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 26.6 ± 8.3 mL/min/1.73 m2. Baseline median serum CPP-I was 14.9 × 104 particles/mL [interquartile range (IQR) 4.6-49.3] and median CPP-II was 3.3 × 103 particles/mL (IQR 1.4-5.4). There was no significant difference between treatment groups at 96 weeks in CPP-I [22.8% (95% confidence interval -39.2, 36.4), P = 0.65] or CPP-II [-18.3% (95% confidence interval -40.0, 11.2), P = 0.20] compared with a placebo. Serum CPP were not correlated with baseline PWV or AAC, or with the progression of either marker.
Conclusions: Lanthanum carbonate was not associated with a reduction of CPP at 96 weeks when compared with a placebo in a CKD cohort.
Keywords: calciprotein particles; cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; mineral metabolism; phosphate binders.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan Det al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1296–1305 - PubMed
-
- Jahnen-Dechent W, Buscher A, Koppert Set al. Mud in the blood: the role of protein-mineral complexes and extracellular vesicles in biomineralisation and calcification. J Struct Biol 2020; 212: 107577. - PubMed
-
- Smith ER, Hewitson TD, Jahnen-Dechent W. Calciprotein particles: mineral behaving badly? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2020; 29: 378–386 - PubMed
-
- Smith ER, Ford ML, Tomlinson LAet al. Phosphorylated fetuin-A-containing calciprotein particles are associated with aortic stiffness and a procalcific milieu in patients with pre-dialysis CKD. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 1957–1966 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous