Reliable Numerical Models of Nickel-Titanium Stents: How to Deduce the Specific Material Properties from Testing Real Devices
- PMID: 35212855
- PMCID: PMC8917046
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-022-02932-1
Reliable Numerical Models of Nickel-Titanium Stents: How to Deduce the Specific Material Properties from Testing Real Devices
Abstract
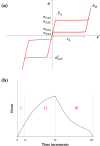
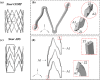
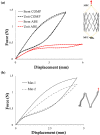
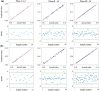
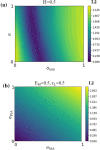
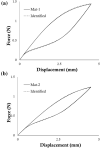
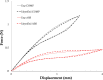
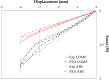
The current interest of those dealing with medical research is the preparation of digital twins. In this frame, the first step to accomplish is the preparation of reliable numerical models. This is a challenging task since it is not common to know the exact device geometry and material properties unless in studies performed in collaboration with the manufacturer. The particular case of modeling Ni-Ti stents can be highlighted as a worst-case scenario due to both the complex geometrical features and non-linear material response. Indeed, if the limitations in the description of the geometry can be overcome, many difficulties still exist in the assessment of the material, which can vary according to the manufacturing process and requires many parameters for its description. The purpose of this work is to propose a coupled experimental and computational workflow to identify the set of material properties in the case of commercially-resembling Ni-Ti stents. This has been achieved from non-destructive tensile tests on the devices compared with results from Finite Element Analysis (FEA). A surrogate modeling approach is proposed for the identification of the material parameters, based on a minimization problem on the database of responses of Ni-Ti materials obtained with FEA with a series of different parameters. The reliability of the final result was validated through the comparison with the output of additional experiments.
Keywords: Digital twin; Material identification; Model validation; Self-expandable stent; Surrogate modeling.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allegretti D, Berti F, Migliavacca F, Pennati G, Petrini L. Fatigue assessment of nickel-titanium peripheral stents: comparison of multi-axial fatigue models. Shape Mem. Superelasticity. 2018;4:186–196. doi: 10.1007/s40830-018-0150-7. - DOI
-
- Arrigoni M, Auricchio F, Cacciafesta V, Petrini L, Pietrabissa R. Mechanical characterisation of orthodontic superelastic Ni-Ti wires. Strain. 2001;11:577–582.
-
- ASME . V&V 40: Assessing Credibility of Computational Modeling Through Verification and Validation: Application to Medical Devices. New York: ASME; 2018.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

