Purification and Isolation of Hepatic Stellate Cells
- PMID: 35212989
- PMCID: PMC8930280
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2128-8_9
Purification and Isolation of Hepatic Stellate Cells
Abstract
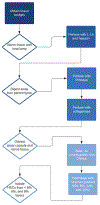
Quiescent human hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) serve as important reservoirs of fat-soluble vitamins in the body, namely vitamin A. In an activated form, HSCs are the drivers of fibrosis following chronic liver injury. In non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) specifically, activated HSCs are drivers of induction and progression of fibrogenesis. Isolation and purification of HSCs from donor liver samples provides an avenue to study HSCs and their fibrotic capabilities. Manual and chemical digestion of donor liver via dissection and Pronase, collagenase, and DNAse treatment creates a suspension of non-parenchymal liver cells. Quiescent HSCs can be further isolated from this suspension by density-gradient centrifugation in a 6%, 8%, 12%, and 15% arabinogalactan medium. After collection of HSCs from the low-density layers of the gradient, they can be grown on uncoated plastic. Rodent HSCs can also be isolated via density-gradient centrifugation. To isolate activated HSCs, liver tissue explants or established immortalized HSC lines can be utilized. Here, we described protocols for isolation of human and rodent HSCs.
Keywords: Arabinogalactan; Density-gradient centrifugation; Hepatic stellate cells; Lipocytes; Vitamin A.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures
References
-
- Geerts A (2001) History, heterogeneity, developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis 21:311–335 - PubMed
-
- Senoo H, Yoshikawa K, Morii M et al. (2010) Hepatic stellate cell (vitamin A-storing cell) and its relative--past, present and future. Cell Biol Int 34:1247–1272 - PubMed
-
- Rockey DC (2001) Hepatic blood flow regulation by stellate cells in normal and injured liver. Semin Liver Dis 21:337–349 - PubMed
-
- Tsuchida T, Friedman SL (2017) Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:397–411 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

