Identification of kidney injury released circulating osteopontin as causal agent of respiratory failure
- PMID: 35213222
- PMCID: PMC8880785
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm5900
Identification of kidney injury released circulating osteopontin as causal agent of respiratory failure
Abstract
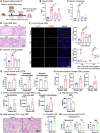
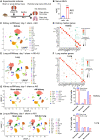
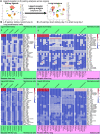
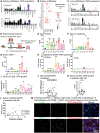
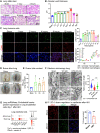
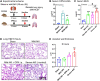
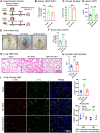
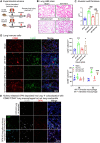
Tissue injury can drive secondary organ injury; however, mechanisms and mediators are not well understood. To identify interorgan cross-talk mediators, we used acute kidney injury (AKI)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) as a clinically important example. Using kidney and lung single-cell RNA sequencing after AKI in mice followed by ligand-receptor pairing analysis across organs, kidney ligands to lung receptors, we identify kidney-released circulating osteopontin (OPN) as a novel AKI-ALI mediator. OPN release from kidney tubule cells triggered lung endothelial leakage, inflammation, and respiratory failure. Pharmacological or genetic OPN inhibition prevented AKI-ALI. Transplantation of ischemic wt kidneys caused AKI-ALI, but not of ischemic OPN-global knockout kidneys, identifying kidney-released OPN as necessary interorgan signal to cause AKI-ALI. We show that OPN serum levels are elevated in patients with AKI and correlate with kidney injury. Our results demonstrate feasibility of using ligand-receptor analysis across organs to identify interorgan cross-talk mediators and may have important therapeutic implications in human AKI-ALI and multiorgan failure.
Figures

References
-
- Teixeira J. P., Ambruso S., Griffin B. R., Faubel S., Pulmonary consequences of acute kidney injury. Semin. Nephrol. 39, 3–16 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

