Mortality of Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 Patients in Traditional versus Expanded Intensive Care Units in New York
- PMID: 35213292
- PMCID: PMC9353963
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202106-705OC
Mortality of Mechanically Ventilated COVID-19 Patients in Traditional versus Expanded Intensive Care Units in New York
Abstract
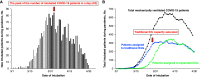
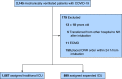
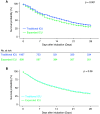
Rationale: During the first wave of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic in New York City, the number of mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients rapidly surpassed the capacity of traditional intensive care units (ICUs), resulting in health systems utilizing other areas as expanded ICUs to provide critical care. Objectives: To evaluate the mortality of patients admitted to expanded ICUs compared with those admitted to traditional ICUs. Methods: Multicenter, retrospective, cohort study of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 admitted to the ICUs at 11 Northwell Health hospitals in the greater New York City area between March 1, 2020 and April 30, 2020. Primary outcome was in-hospital mortality up to 28 days after intubation of COVID-19 patients. Results: Among 1,966 mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19, 1,198 (61%) died within 28 days after intubation, 46 (2%) were transferred to other hospitals outside of the Northwell Health system, 722 (37%) survived in the hospital until 28 days or were discharged after recovery. The risk of mortality of mechanically ventilated patients admitted to expanded ICUs was not different from those admitted to traditional ICUs (hazard ratio [HR], 1.07; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.95-1.20; P = 0.28), while hospital occupancy for critically ill patients itself was associated with increased risk of mortality (HR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.12-1.45; P < 0.001). Conclusions: Although increased hospital occupancy for critically ill patients itself was associated with increased mortality, the risk of 28-day in-hospital mortality of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 who were admitted to expanded ICUs was not different from those admitted to traditional ICUs.
Keywords: COVID pandemic; expanded ICU; hospital occupancy for critically ill patients; mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients; traditional ICU.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply: COVID-19 Mortality Differences: Patient-related Data and Intensive Care Unit Load Are Prerequisites.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022 Sep;19(9):1624-1625. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202204-313LE. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022. PMID: 35522443 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 Mortality Differences: Patient-related Data and Intensive Care Unit Load Are Prerequisites.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022 Sep;19(9):1622-1623. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202203-230LE. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022. PMID: 35522444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Understanding the Impact of Intensive Care Unit Personnel on Intensive Care Unit Mortality during Times of High Demand.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022 Sep;19(9):1623-1624. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202203-231LE. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022. PMID: 35522445 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Weinberger DM Cohen T Crawford FW Mostashari F Olson D Pitzer VE et al.Estimating the early death toll of COVID-19 in the United States medRxiv 2020https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.15.20066431v2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

