Accessible, fast and easy fabrication of hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic microdroplet arrays
- PMID: 35213568
- PMCID: PMC8880433
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263282
Accessible, fast and easy fabrication of hydrophilic-in-hydrophobic microdroplet arrays
Abstract
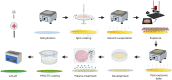
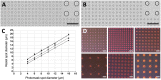
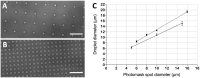
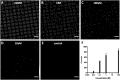
Microdroplet arrays (MDAs) are powerful tools for digital immunoassays, high-throughput screening and single cell analysis. However, MDAs are usually produced with cleanroom processes, which are associated with high costs and low availability. Furthermore, in order to obtain robust and stable MDAs based on hydrophilic spots surrounded by a hydrophobic background, the chemistry must be strictly controlled, which is challenging using shared equipment. Here, we developed a new method to fabricate MDA substrates independently from the cleanroom. A small and low-cost in-house built system to collimate the light source was assembled for photopatterning a negative resist, and spots with diameters down to 4 μm were obtained, with only 3% to 5% spot-to-spot variation across the same sample and high batch-to-batch reproducibility. The use of a negative photoresist enabled the formation of a hydrophobic coating in solution which yielded high-quality MDAs. The feasibility for carrying out digital assays was demonstrated by measuring anti-Tau antibody in sample buffers containing bovine serum albumin, with no noticeable surface fouling. The reported, robust, cost-effective, and fast process could hence lower the threshold to fabricate and use MDAs for digital immunoassays and other microcompartmentalization-based applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Photolithographic Patterning of FluorAcryl for Biphilic Microwell-Based Digital Bioassays and Selection of Bacteria.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Sep 22;13(37):43914-43924. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c10096. Epub 2021 Sep 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34491739
-
Single-Step Fabrication of High-Density Microdroplet Arrays of Low-Surface-Tension Liquids.Adv Mater. 2016 Apr;28(16):3202-8. doi: 10.1002/adma.201505972. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Adv Mater. 2016. PMID: 26915480
-
Micro-droplet arrays for micro-compartmentalization using an air/water interface.Lab Chip. 2018 Sep 11;18(18):2797-2805. doi: 10.1039/c8lc00608c. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 30123911
-
New fabrication and applications of carbohydrate arrays.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(3):288-95. doi: 10.2174/09298673113206660267. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24059231 Review.
-
Carbon Substrates: A Stable Foundation for Biomolecular Arrays.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2015;8:263-85. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-071114-040146. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2015. PMID: 26048550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rotman B. Measurement of activity of single molecules of beta-D-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States [Internet]. 1961. [cited 2021 Jan 6];47(12):1981–91. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC223251/ doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.1981 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahrberg CD, Lee JM, Chung BG. Microwell Array-based Digital PCR for Influenza Virus Detection. Biochip J. 2019;13(3):269–76.
-
- Li M, Van Zee M, Goda K, Di Carlo D. Size-based sorting of hydrogel droplets using inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip [Internet]. 2018. Sep 7 [cited 2021 Jan 16];18(17):2575–82. Available from: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2018/lc/c8lc00568k doi: 10.1039/c8lc00568k - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

