Pediatric growth hormone treatment in Italy: A systematic review of epidemiology, quality of life, treatment adherence, and economic impact
- PMID: 35213607
- PMCID: PMC8880399
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264403
Pediatric growth hormone treatment in Italy: A systematic review of epidemiology, quality of life, treatment adherence, and economic impact
Abstract
Objectives: This systematic review aims to describe 1) the epidemiology of the diseases indicated for treatment with growth hormone (GH) in Italy; 2) the adherence to the GH treatment in Italy and factors associated with non-adherence; 3) the economic impact of GH treatment in Italy; 4) the quality of life of patients treated with GH and their caregivers in Italy.
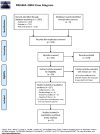
Methods: Systematic literature searches were performed in PubMed, Embase and Web of Science from January 2010 to March 2021. Literature selection process, data extraction and quality assessment were performed by two independent reviewers. Study protocol has been registered in PROSPERO (CRD42021240455).
Results: We included 25 studies in the qualitative synthesis. The estimated prevalence of growth hormone deficiency (GHD) was 1/4,000-10,000 in the general population of children; the prevalence of Short Stature HOmeoboX Containing gene deficiency (SHOX-D) was 1/1,000-2,000 in the general population of children; the birth prevalence of Turner syndrome was 1/2,500; the birth prevalence of Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) was 1/15,000. Treatment adherence was suboptimal, with a range of non-adherent patients of 10-30%. The main reasons for suboptimal adherence were forgetfulness, being away from home, pain/discomfort caused by the injection. Economic studies reported a total cost for a complete multi-year course of GH treatment of almost 100,000 euros. A study showed that drug wastage can amount up to 15% of consumption, and that in some Italian regions there could be a considerable over- or under-prescribing. In general, patients and caregivers considered the GH treatment acceptable. There was a general satisfaction among patients with regard to social and school life and GH treatment outcomes, while there was a certain level of intolerance to GH treatment among adolescents. Studies on PWS patients and their caregivers showed a lower quality of life compared to the general population, and that social stigma persists.
Conclusion: Growth failure conditions with approved GH treatment in Italy constitute a significant burden of disease in clinical, social, and economic terms. GH treatment is generally considered acceptable by patients and caregivers. The total cost of the GH treatment is considerable; there are margins for improving efficiency, by increasing adherence, reducing drug wastage and promoting prescriptive appropriateness.
Conflict of interest statement
Simona Granato, Giuseppe Novelli, Roberto Di Virgilio and Daria La Torre are employees of Pfizer. Barbara Polistena declares to have received in the last 5 years payments or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from the following commercial sources: Allergan, Amgen, Astellas, Baxter, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag, Jazzpharma, Mylan, Nestlé HS, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Shire, Takeda, Teva; in addition, she received consulting fees from UCB. Federico Spandonaro declares to have received in the last 5 years payments or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from the following commercial sources: Allergan, Amgen, Astellas, Baxter, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag, Jazzpharma, Mylan, Nestlé HS, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Shire, Takeda, Teva; in addition, he received consulting fees from Amgen. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
References
-
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (2018). CASP Cohort Study Checklist. [online] Available at: https://casp-uk.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CASP-Cohort-Study-Checkli.... Accessed: 04/03/2021.
-
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (2018). CASP Qualitative Checklist. [online] Available at: https://casp-uk.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CASP-Qualitative-Checklis.... Accessed: 04/03/2021.
-
- Institute of Health Economics (IHE). Quality Appraisal of Case Series Studies Checklist. Edmonton (AB): Institute of Health Economics; 2014. Available from: http://www.ihe.ca/research-programs/rmd/cssqac/cssqac-about.
-
- Evers S, Goossens M, de Vet H, van Tulder M, Ament A. Criteria list for assessment of methodological quality of economic evaluations: Consensus on Health Economic Criteria. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2005;21(2):240–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials