Relationship between HbA1c, fructosamine and clinical assessment of glycemic control in dogs
- PMID: 35213623
- PMCID: PMC8880912
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264275
Relationship between HbA1c, fructosamine and clinical assessment of glycemic control in dogs
Abstract
Background: Serum fructosamine is a routine test used for clinical monitoring of diabetes mellitus (DM) but the usefulness of HbA1c for this purpose has not been extensively studied.
Hypothesis: The study aimed to compare the ability of blood HbA1c and serum fructosamine tests to correctly classify DM control determined using a clinically-based assessment.
Animals: 28 client-owned dogs with naturally-occurring diabetes mellitus.
Methods: Cross-sectional observational study. Ability of fructosamine and HbA1c tests to classify diabetes control in dogs was determined.
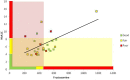
Results: Clinical assessment classified 50% of dogs as having good diabetic control and 82% as having acceptable diabetic control. Analysis using Cohen's kappa test showed that agreements between fructosamine and HbA1c results and the clinical assessment ranged from poor to fair. Fructosamine and HbA1c results from each dog showed a moderate correlation. Overall, the HbA1c test showed the best agreement with the clinical assessment when diabetes control was considered either acceptable or unacceptable, although the strength of agreement was considered fair (kappa = 0.27).
Conclusions and clinical importance: The HbA1c concentration was found to be more consistent with clinical evaluation of diabetes control than was the serum fructosamine concentration. The HbA1c level is a useful tool for assessment of glycemic status in diabetic dogs but should be used alongside other tests for outpatient monitoring of clinically stable diabetic dogs.
Conflict of interest statement
TS received financial and material support from Baycom Diagnostics (https://baycomdiagnostics.com), which developed, markets, and performs the commercial HbA1c assay studied as part of this project. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

