Multiple subregions within the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibit fibrosis, microvascular leakage, and monocyte migration
- PMID: 35213624
- PMCID: PMC8880820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264413
Multiple subregions within the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibit fibrosis, microvascular leakage, and monocyte migration
Abstract
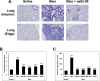
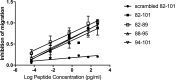
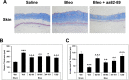
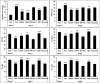
The caveolin-1 scaffolding domain (CSD, amino acids 82-101 of caveolin-1) has been shown to suppress bleomycin-induced lung and skin fibrosis and angiotensin II (AngII)-induced myocardial fibrosis. To identify active subregions within CSD, we split its sequence into three slightly overlapping 8-amino acid subregions (82-89, 88-95, and 94-101). Interestingly, all three peptides showed activity. In bleomycin-treated mice, all three subregions suppressed the pathological effects on lung and skin tissue morphology. In addition, while bone marrow monocytes isolated from bleomycin-treated mice showed greatly enhanced migration in vitro toward CXCL12, treatment in vivo with CSD and its subregions almost completely suppressed this enhanced migration. In AngII-induced heart failure, both 82-89 and 88-95 significantly suppressed fibrosis (both Col I and HSP47 levels), microvascular leakage, and heart weight/ body weight ratio (HW/BW) while improving ventricular function. In contrast, while 94-101 suppressed the increase in Col I, it did not improve the other parameters. The idea that all three subregions can be active depending on the assay was further supported by experiments studying the in vitro migration of human monocytes in which all three subregions were extremely active. These studies are very novel in that it has been suggested that there is only one active region within CSD that is centered on amino acids 90-92. In contrast, we demonstrate here the presence of other active regions within CSD.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded in part by a Sponsored Research Agreement from Lung Therapeutics, Inc., to Dr. Stanley Hoffman. Lung Therapeutics has also licensed a use patent (no. 8,058,227) issued to the Medical University of South Carolina for the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide as a treatment for fibrotic diseases on which Drs. Hoffman and Tourkina are named coinventors. Lung Therapeutics played no role in the study design; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; writing of the paper; and/or decision to submit for publication and only provided financial support in the form of authors’ salaries [SH, ET, DK, PC] and research materials. Our partial funding by Lung Therapeutics does not affect our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of angiotensin II-induced pathological changes in heart and kidney by the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 21;13(12):e0207844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207844. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30576317 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 regulates leucocyte behaviour in fibrotic lung disease.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jun;69(6):1220-6. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.117580. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 20410070 Free PMC article.
-
The Caveolin-1 Scaffolding Domain Peptide Reverses Aging-Associated Deleterious Changes in Multiple Organs.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021 Jul;378(1):1-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.000424. Epub 2021 Apr 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021. PMID: 33879542
-
Role of caveolin-1 in fibrotic diseases.Matrix Biol. 2013 Aug 8;32(6):307-15. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.03.005. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23583521 Review.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Caveolin-1 in Sepsis - A Mini-Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 15;13:902907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902907. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin Scaffolding Domain (CSD) Peptide LTI-2355 Modulates the Phagocytic and Synthetic Activity of Lung-Derived Myeloid Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) and Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID Fibrosis (PASC-F).Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 26;13(4):796. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040796. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299362 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of caveolin-1 in skin diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1035451. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035451. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing Autoimmune Research: The Role of Caveolin-1.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Aug;13(8):e70230. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70230. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40778471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Brain Endothelial Cell Caveolin-1/CXCL10 Axis Promotes T Cell Transcellular Migration Across the Blood-Brain Barrier.ASN Neuro. 2025;17(1):2472070. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2025.2472070. Epub 2025 Mar 10. ASN Neuro. 2025. PMID: 40063988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhandary YP, Shetty SK, Marudamuthu AS, Gyetko MR, Idell S, Gharaee-Kermani M, et al.. Regulation of alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis and pulmonary fibrosis by coordinate expression of components of the fibrinolytic system. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302(5):L463–73. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00099.2011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

