The effect of TNF-α inhibitor treatment on microRNAs and endothelial function in collagen induced arthritis
- PMID: 35213638
- PMCID: PMC8880872
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264558
The effect of TNF-α inhibitor treatment on microRNAs and endothelial function in collagen induced arthritis
Abstract
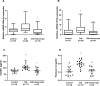
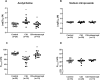
Chronic inflammation causes dysregulated expression of microRNAs. Aberrant microRNA expression is associated with endothelial dysfunction. In this study we determined whether TNF-α inhibition impacted the expression of miRNA-146a-5p and miRNA-155-5p, and whether changes in the expression of these miRNAs were related to inflammation-induced changes in endothelial function in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Sixty-four Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into control (n = 24), CIA (n = 24) and CIA+etanercept (n = 16) groups. CIA and CIA+etanercept groups were immunized with bovine type-II collagen, emulsified in incomplete Freund's adjuvant. Upon signs of arthritis, the CIA+etanercept group received 10mg/kg of etanercept intraperitoneally, every three days. After six weeks of treatment, mesenteric artery vascular reactivity was assessed using wire-myography. Serum concentrations of TNF-α, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and pentraxin-3 (PTX-3) were measured by ELISA. Relative expression of circulating miRNA-146a-5p and miRNA-155-5p were determined using RT-qPCR. Compared to controls, circulating miRNA-155-5p, VCAM-1 and PTX-3 concentrations were increased, and vessel relaxation was impaired in the CIA (all p<0.05), but not in the CIA+etanercept (all p<0.05) groups. The CIA group had greater miRNA-146a-5p expression compared to the CIA+etanercept group (p = 0.005). Independent of blood pressure, miRNA-146a-5p expression was associated with increased PTX-3 concentrations (p = 0.03), while miRNA-155-5p expression was associated with impaired vessel relaxation (p = 0.01). In conclusion, blocking circulating TNF-α impacted systemic inflammation-induced increased expression of miRNA-146a-5p and miRNA-155-5p, which were associated with endothelial inflammation and impaired endothelial dependent vasorelaxation, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

