Ppe.XapF: High throughput KASP assays to identify fruit response to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni (Xap) in peach
- PMID: 35213640
- PMCID: PMC8880879
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264543
Ppe.XapF: High throughput KASP assays to identify fruit response to Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni (Xap) in peach
Abstract
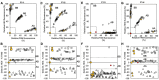
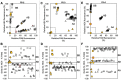
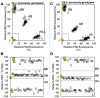
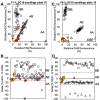
Bacterial spot, caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni (Xap), is a serious peach disease with symptoms that traverse severe defoliation and black surface pitting, cracking or blemishes on peach fruit with global economic impacts. A management option for control and meeting consumer demand for chemical-free, environmentally friendly fruit production is the development of resistant or tolerant cultivars. We developed simple, accurate, and efficient DNA assays (Ppe.XapF) based on SNP genotyping with KASP technology to quickly test for bacterial spot resistance alleles in peach fruit that allows breeders to cull seedlings at the greenhouse stage. The objective of this research was to validate newly developed DNA tests that target the two major QTLs for fruit resistance in peach with diagnostic utility in predicting fruit response to bacterial spot infection. Our study confirms that with only two Ppe.XapF DNA tests, Ppe.XapF1-1 and Ppe.XapF6-2, individuals carrying susceptible alleles can be identified. Use of these efficient and accurate Ppe.XapF KASP tests resulted in 44% reduction in seedling planting rate in the Clemson University peach breeding program.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bassi D, Monet Rene. Botany and Taxonomy. In: Layne DR, Bassi D, editors. The Peach: Botany, Production and Use. London, UK.: CABI; 2008. pp. 1–36.
-
- Abdelghafar A, Burrell R, Reighard G, Gasic K. Antioxidant capacity and bioactive compounds accumulation in peach breeding germplasm. J Am Pom Soc. 2018;72: 40–69.
-
- FAOSTAT. Crops Data. 2019. Available: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC.
-
- Byrne DH. Trends in stone fruit cultivar development. HortTech. 2005;15: 494–500.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

