Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals excitotoxicity associated with outcome after ischaemic stroke
- PMID: 35213696
- PMCID: PMC9890452
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac080
Multi-ancestry GWAS reveals excitotoxicity associated with outcome after ischaemic stroke
Abstract
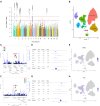
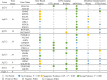
During the first hours after stroke onset, neurological deficits can be highly unstable: some patients rapidly improve, while others deteriorate. This early neurological instability has a major impact on long-term outcome. Here, we aimed to determine the genetic architecture of early neurological instability measured by the difference between the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) within 6 h of stroke onset and NIHSS at 24 h. A total of 5876 individuals from seven countries (Spain, Finland, Poland, USA, Costa Rica, Mexico and Korea) were studied using a multi-ancestry meta-analyses. We found that 8.7% of NIHSS at 24 h of variance was explained by common genetic variations, and also that early neurological instability has a different genetic architecture from that of stroke risk. Eight loci (1p21.1, 1q42.2, 2p25.1, 2q31.2, 2q33.3, 5q33.2, 7p21.2 and 13q31.1) were genome-wide significant and explained 1.8% of the variability suggesting that additional variants influence early change in neurological deficits. We used functional genomics and bioinformatic annotation to identify the genes driving the association from each locus. Expression quantitative trait loci mapping and summary data-based Mendelian randomization indicate that ADAM23 (log Bayes factor = 5.41) was driving the association for 2q33.3. Gene-based analyses suggested that GRIA1 (log Bayes factor = 5.19), which is predominantly expressed in the brain, is the gene driving the association for the 5q33.2 locus. These analyses also nominated GNPAT (log Bayes factor = 7.64) ABCB5 (log Bayes factor = 5.97) for the 1p21.1 and 7p21.1 loci. Human brain single-nuclei RNA-sequencing indicates that the gene expression of ADAM23 and GRIA1 is enriched in neurons. ADAM23, a presynaptic protein and GRIA1, a protein subunit of the AMPA receptor, are part of a synaptic protein complex that modulates neuronal excitability. These data provide the first genetic evidence in humans that excitotoxicity may contribute to early neurological instability after acute ischaemic stroke.
Keywords: NIHSS; genetics; ischaemic stroke; neuroprotection.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Update of
-
Multi-ancestry genetic study in 5,876 patients identifies an association between excitotoxic genes and early outcomes after acute ischemic stroke.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Nov 3:2020.10.29.20222257. doi: 10.1101/2020.10.29.20222257. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Brain. 2022 Jul 29;145(7):2394-2406. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac080. PMID: 33173895 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Advances in the genetics of stroke risk and recovery.J Neurol. 2023 Jan;270(1):590-591. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11525-w. Epub 2022 Dec 22. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36547717 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . The global burden of disease: 2004 update. World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67–e492. - PubMed
-
- Farooq MU, Chaudhry AH, Amin K, Majid A. The WHO STEPwise approach to stroke surveillance. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008;18(10):665. - PubMed
-
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24):1581–1587. - PubMed

