Oligonucleotide Solid Nucleolipid Nanoparticles against Antibiotic Resistance of ESBL-Producing Bacteria
- PMID: 35214036
- PMCID: PMC8876242
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020299
Oligonucleotide Solid Nucleolipid Nanoparticles against Antibiotic Resistance of ESBL-Producing Bacteria
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nguyen et al. Oligonucleotide Solid Nucleolipid Nanoparticles against Antibiotic Resistance of ESBL-Producing Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 299.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 28;14(11):2317. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112317. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365257 Free PMC article.
Abstract
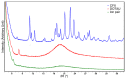
Antibiotic resistance has become a major issue in the global healthcare system, notably in the case of Gram-negative bacteria. Recent advances in technology with oligonucleotides have an enormous potential for tackling this problem, providing their efficient intrabacterial delivery. The current work aimed to apply this strategy by using a novel nanoformulation consisting of DOTAU, a nucleolipid carrier, in an attempt to simultaneously deliver antibiotic and anti-resistance oligonucleotides. Ceftriaxone, a third-generation cephalosporin, was formulated with DOTAU to form an ion pair, and was then nanoprecipitated. The obtained solid nanocapsules were characterized using FT-IR, XRD, HPLC, TEM and DLS techniques and further functionalized by the anti-resistance ONα sequence. To obtain an optimal anti-resistance activity and encapsulation yield, both the formulation protocol and the concentration of ONα were optimized. As a result, monodispersed negatively charged nanoparticles of CFX-DOTAU-ONα with a molar ratio of 10:24:1 were obtained. The minimum inhibitory concentration of these nanoparticles on the resistant Escherichia coli strain was significantly reduced (by 75%) in comparison with that of non-vectorized ONα. All aforementioned results reveal that our nanoformulation can be considered as an efficient and relevant strategy for oligonucleotide intrabacterial delivery in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: CTX-M15 ß-lactamase; ESBL-producing E. coli; antibiotic resistance; nanocapsules; nucleic acids; nucleolipid; oligonucleotides; solid nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations. Rev. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016:1–84. doi: 10.4103/2045-080x.186181. - DOI
-
- WHO . Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Batceria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

