Advancing towards Ubiquitous EEG, Correlation of In-Ear EEG with Forehead EEG
- PMID: 35214468
- PMCID: PMC8879675
- DOI: 10.3390/s22041568
Advancing towards Ubiquitous EEG, Correlation of In-Ear EEG with Forehead EEG
Abstract
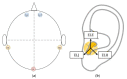
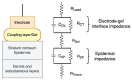
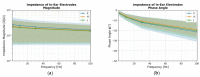
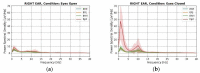
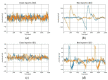
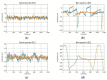
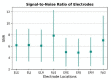
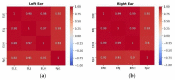
Wearable EEG has gained popularity in recent years driven by promising uses outside of clinics and research. The ubiquitous application of continuous EEG requires unobtrusive form-factors that are easily acceptable by the end-users. In this progression, wearable EEG systems have been moving from full scalp to forehead and recently to the ear. The aim of this study is to demonstrate that emerging ear-EEG provides similar impedance and signal properties as established forehead EEG. EEG data using eyes-open and closed alpha paradigm were acquired from ten healthy subjects using generic earpieces fitted with three custom-made electrodes and a forehead electrode (at Fpx) after impedance analysis. Inter-subject variability in in-ear electrode impedance ranged from 20 kΩ to 25 kΩ at 10 Hz. Signal quality was comparable with an SNR of 6 for in-ear and 8 for forehead electrodes. Alpha attenuation was significant during the eyes-open condition in all in-ear electrodes, and it followed the structure of power spectral density plots of forehead electrodes, with the Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.92 between in-ear locations ELE (Left Ear Superior) and ERE (Right Ear Superior) and forehead locations, Fp1 and Fp2, respectively. The results indicate that in-ear EEG is an unobtrusive alternative in terms of impedance, signal properties and information content to established forehead EEG.
Keywords: BCI; biopotential electrodes; correlation; forehead EEG; impedance spectroscopy; in-ear EEG.
Conflict of interest statement
The research work was carried out as a Master’s thesis project at IDUN Technologies AG, where Swati Mandekar, Abigail Holland, Moritz Thielen and Mark Melnykowycz were employed during the research study.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Signal quality evaluation of an in-ear EEG device in comparison to a conventional cap system.Front Neurosci. 2024 Sep 10;18:1441897. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1441897. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39319310 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Electrode Materials for Scalp, Forehead, and Ear EEG: A Mini-Review.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Aug 21;6(8):3019-3032. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00322. Epub 2023 Jul 26. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37493408 Review.
-
Physiological artifacts in scalp EEG and ear-EEG.Biomed Eng Online. 2017 Aug 11;16(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12938-017-0391-2. Biomed Eng Online. 2017. PMID: 28800744 Free PMC article.
-
Towards emerging EEG applications: a novel printable flexible Ag/AgCl dry electrode array for robust recording of EEG signals at forehead sites.J Neural Eng. 2020 Mar 4;17(2):026001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab71ea. J Neural Eng. 2020. PMID: 32000145
-
The future of wearable EEG: a review of ear-EEG technology and its applications.J Neural Eng. 2023 Oct 6;20(5). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acfcda. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 37748474 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of motor-related mu rhythm desynchronization by ear EEG.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 8;20(4):e0321107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321107. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40198632 Free PMC article.
-
Signal quality evaluation of an in-ear EEG device in comparison to a conventional cap system.Front Neurosci. 2024 Sep 10;18:1441897. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1441897. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39319310 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Wearable Neuroimaging Devices for Health Monitoring and Neurophenotyping: A Scoping Review.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Apr 16;9(4):237. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9040237. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalas M.S., Momin B.F. Stress Detection and Reduction using EEG Signals; Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT); Chennai, India. 3–5 March 2016.
-
- Marketwatch PressRelease Brain Monitoring Devices Global Market: Global Industry, Trends, Market Size, Forecast up to 2030. [(accessed on 7 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.marketwatch.com/press-release/brain-monitoring-devices-globa....
-
- The Insight Partners EEG Devices Market to Grow at a CAGR of 7.5% to Reach US $1699.52 Million from 2021 to 2028. 2021. [(accessed on 7 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/reports/eeg-devices-market/
-
- Yao S., Zhu Y. Nanomaterial-Enabled Dry Electrodes for Electrophysiological Sensing: A Review. JOM. 2016;68:1145–1155. doi: 10.1007/s11837-016-1818-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

