Multi-Method Diagnosis of Blood Microscopic Sample for Early Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on Deep Learning and Hybrid Techniques
- PMID: 35214531
- PMCID: PMC8876170
- DOI: 10.3390/s22041629
Multi-Method Diagnosis of Blood Microscopic Sample for Early Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on Deep Learning and Hybrid Techniques
Abstract
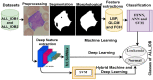
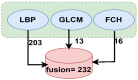
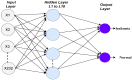
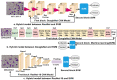
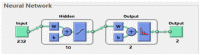
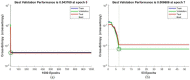
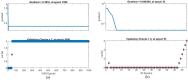
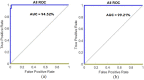
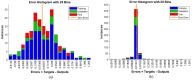
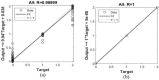
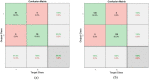
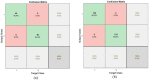
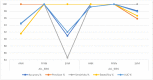
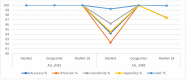
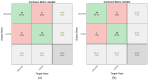
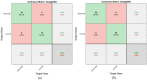
Leukemia is one of the most dangerous types of malignancies affecting the bone marrow or blood in all age groups, both in children and adults. The most dangerous and deadly type of leukemia is acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It is diagnosed by hematologists and experts in blood and bone marrow samples using a high-quality microscope with a magnifying lens. Manual diagnosis, however, is considered slow and is limited by the differing opinions of experts and other factors. Thus, this work aimed to develop diagnostic systems for two Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Image Databases (ALL_IDB1 and ALL_IDB2) for the early detection of leukemia. All images were optimized before being introduced to the systems by two overlapping filters: the average and Laplacian filters. This study consists of three proposed systems as follows: the first consists of the artificial neural network (ANN), feed forward neural network (FFNN), and support vector machine (SVM), all of which are based on hybrid features extracted using Local Binary Pattern (LBP), Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and Fuzzy Color Histogram (FCH) methods. Both ANN and FFNN reached an accuracy of 100%, while SVM reached an accuracy of 98.11%. The second proposed system consists of the convolutional neural network (CNN) models: AlexNet, GoogleNet, and ResNet-18, based on the transfer learning method, in which deep feature maps were extracted and classified with high accuracy. All the models obtained promising results for the early detection of leukemia in both datasets, with an accuracy of 100% for the AlexNet, GoogleNet, and ResNet-18 models. The third proposed system consists of hybrid CNN-SVM technologies, consisting of two blocks: CNN models for extracting feature maps and the SVM algorithm for classifying feature maps. All the hybrid systems achieved promising results, with AlexNet + SVM achieving 100% accuracy, Goog-LeNet + SVM achieving 98.1% accuracy, and ResNet-18 + SVM achieving 100% accuracy.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; convolutional neural network; fuzzy color histogram; gray level co-occurrence matrix; hybrid method; local binary pattern; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


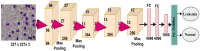

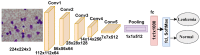
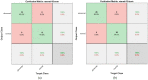
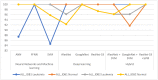
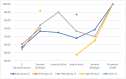
References
-
- Al-Hafiz F., Al-Megren S., Kurdi H. Red blood cell segmentation by thresholding and Canny detector. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018;141:327–334. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.193. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

