Autochthonous Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Booster-Vaccinated (3 Doses) Healthcare Workers in Southern Italy: Just the Tip of the Iceberg?
- PMID: 35214741
- PMCID: PMC8880534
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10020283
Autochthonous Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Booster-Vaccinated (3 Doses) Healthcare Workers in Southern Italy: Just the Tip of the Iceberg?
Abstract
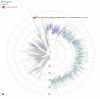
The Omicron variant of concern (VOC), first detected in Italy at the end of November 2021, has since spread rapidly, despite high vaccine coverage in the Italian population, especially in healthcare workers (HCWs). This study describes an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection in 15 booster-vaccinated HCWs. On 16 December 2021, two HCWs working in the same ward were infected with SARS-CoV-2. The Omicron VOC was suspected due to S gene target failure on molecular testing. Further investigation revealed that 15 (65%) of 23 HCWs attending a social gathering on 13 December were infected with Omicron, as shown by whole-genome sequencing, with a phylogenetic tree suggesting a common source of exposure. Five of these HCWs experienced mild symptoms. A patient with multiple chronic conditions hospitalized in the same ward was also infected by one of the HCWs involved in the outbreak. Despite being booster vaccinated, this patient required ICU treatment. Ten subjects achieved negativity in 10-19 days. The outbreak in booster-vaccinated subjects confirms the high transmissibility and immune evasion of the Omicron VOC. More stringent non-pharmaceutical interventions, administration of booster doses, and genomic surveillance are crucial long-term strategies to mitigate the consequences of the spread of the Omicron VOC.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Italy; SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant; epidemiology; hospitalization; outbreak; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.....
-
- Network for Genomic Surveillance in South Africa NGS-SA: Updates, COVID-19 Analysis, Narratives, Reports. Durban: NGS-SA. 2021. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ngs-sa.org/ngs-sa_updates_covid-19_analysis_narratives_repor....
-
- World Health Organization Enhancing Readiness for Omicron (B.1.1.529): Technical Brief and Priority Actions for Member States. 2021. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/enhancing-readiness-for-omicron-....
-
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control Rapid Increase of a SARS-CoV-2 Variant with Multiple Spike Protein Mutations Observed in the United Kingdom. Dec 20, 2020. [(accessed on 20 January 2022)]. Threat Assessment Brief. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/threat-assessment-brief-....
-
- Rambaut A. Preliminary Genomic Characterisation of an Emergent SARS-CoV-2 Lineage in the UK Defined by a Novel Set of Spike Mutations—SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus/nCoV-2019 Genomic Epidemiology, Virological. 2020. [(accessed on 30 January 2021)]. Available online: https://virological.org/t/preliminary-genomic-characterisation-of-an-eme....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

