Nanomaterial Probes for Nuclear Imaging
- PMID: 35214911
- PMCID: PMC8875160
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12040582
Nanomaterial Probes for Nuclear Imaging
Abstract
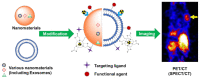
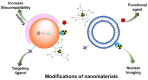
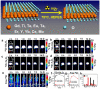
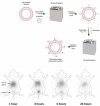
Nuclear imaging is a powerful non-invasive imaging technique that is rapidly developing in medical theranostics. Nuclear imaging requires radiolabeling isotopes for non-invasive imaging through the radioactive decay emission of the radionuclide. Nuclear imaging probes, commonly known as radiotracers, are radioisotope-labeled small molecules. Nanomaterials have shown potential as nuclear imaging probes for theranostic applications. By modifying the surface of nanomaterials, multifunctional radio-labeled nanomaterials can be obtained for in vivo biodistribution and targeting in initial animal imaging studies. Various surface modification strategies have been developed, and targeting moieties have been attached to the nanomaterials to render biocompatibility and enable specific targeting. Through integration of complementary imaging probes to a single nanoparticulate, multimodal molecular imaging can be performed as images with high sensitivity, resolution, and specificity. In this review, nanomaterial nuclear imaging probes including inorganic nanomaterials such as quantum dots (QDs), organic nanomaterials such as liposomes, and exosomes are summarized. These new developments in nanomaterials are expected to introduce a paradigm shift in nuclear imaging, thereby creating new opportunities for theranostic medical imaging tools.
Keywords: molecular imaging probe; nanomaterials; nanoparticles; nuclear imaging; theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiolabeled Liposomes for Nuclear Imaging Probes.Molecules. 2023 Apr 28;28(9):3798. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093798. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticulate Contrast Agents for Multimodality Molecular Imaging.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016 Aug;12(8):1553-84. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2016.2258. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 29341579 Review.
-
An overview of nanoscale radionuclides and radiolabeled nanomaterials commonly used for nuclear molecular imaging and therapeutic functions.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019 Jan;107(1):251-285. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36550. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019. PMID: 30358098 Review.
-
Positron emission tomography imaging using radiolabeled inorganic nanomaterials.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Feb 17;48(2):286-94. doi: 10.1021/ar500362y. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25635467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optically active organic and inorganic nanomaterials for biological imaging applications: A review.Micron. 2023 Sep;172:103486. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2023.103486. Epub 2023 May 24. Micron. 2023. PMID: 37262930 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Innovations and Nano-Delivery of Actinium-225: A Narrative Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 13;15(6):1719. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061719. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic methods for pancreatic cancer and their clinical applications (Review).Oncol Lett. 2025 May 27;30(1):370. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15116. eCollection 2025 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40496545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theranostics with photodynamic therapy for personalized medicine: to see and to treat.Theranostics. 2023 Oct 9;13(15):5501-5544. doi: 10.7150/thno.87363. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37908729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiolabeled Liposomes for Nuclear Imaging Probes.Molecules. 2023 Apr 28;28(9):3798. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093798. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Nanogels: From Drug Carriers to Radiopharmaceutical Agents.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jan;13(1):e2301404. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301404. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 37717209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Truijman M.T., Kwee R.M., van Hoof R.H., Hermeling E., van Oostenbrugge R.J., Mess W.H., Backes W.H., Daemen M.J., Bucerius J., Wildberger J.E., et al. Combined 18 F-FDG PET-CT and DCE-MRI to Assess Inflammation and Microvascularization in Atherosclerotic Plaques. Stroke. 2013;44:3568–3570. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003140. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

