Synthesis and Characterization of Silver-Gold Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Random Lasing
- PMID: 35214936
- PMCID: PMC8879745
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12040607
Synthesis and Characterization of Silver-Gold Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Random Lasing
Abstract
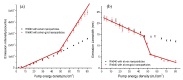
We developed rough silver-gold bimetallic nanoparticles for random lasing. Silver nanoparticles were synthesized based on a citrate-reduction method and the gold (III) chloride trihydrate was added to produce bimetallic nanoparticles. Gold atoms were deposited on the surface of the silver (Ag) through galvanic replacement reactions after the solution was stored at room temperature. Sample characterization and a spectrometry experiment were performed where bimetallic nanoparticles with nanogaps and the extinction of the nanoparticles were observed. The aim of this research is to synthesize nanoparticles for random dye laser in a weakly scattering regime. The novel bimetallic nanoparticles were added to Rhodamine 640 solution to produce random lasing. We found that random dye laser with bimetallic nanoparticles produced spectral narrowing and lasing threshold compared to random dye laser with silver nanoparticles. We attribute that to the localized surface plasmon effects which increase local electromagnetic field to provide sufficient optical gain for random lasing. The rough surface of bimetallic nanoparticles also contributes to the properties of random lasing. Thus, we suggest that the rough bimetallic nanoparticles can be used to develop random lasers.
Keywords: and random lasers; bimetallic; localized surface plasmon effects; nanomaterial; surface roughness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Laser assisted synthesis of anisotropic metal nanocrystals and strong light-matter coupling in decahedral bimetallic nanocrystals.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Jan 19;3(6):1674-1681. doi: 10.1039/d0na00829j. eCollection 2021 Mar 23. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36132566 Free PMC article.
-
Bimetallic structure fabricated by laser interference lithography for tuning surface plasmon resonance.Opt Express. 2008 Jul 7;16(14):10701-9. doi: 10.1364/oe.16.010701. Opt Express. 2008. PMID: 18607486
-
Random Lasing via Plasmon-Induced Cavitation of Microbubbles.Nano Lett. 2021 Jul 28;21(14):6064-6070. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01321. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Nano Lett. 2021. PMID: 34240608
-
Silver-gold bimetallic nanoparticles and their applications as optical materials.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014 Feb;14(2):1563-77. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.9077. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24749442 Review.
-
Fabrication of Au-Ag Bimetallic Nanoparticles Using Pulsed Laser Ablation for Medical Applications: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;13(22):2940. doi: 10.3390/nano13222940. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polarized and Evanescent Guided Wave Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy of Ligand Interactions on a Plasmonic Nanoparticle Optical Chemical Bench.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;14(9):409. doi: 10.3390/bios14090409. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39329784 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Monitoring Water Quality Based on Various Sensing Methods: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 28;19(21):14080. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114080. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36360992 Free PMC article.
-
Properties and Applications of Random Lasers as Emerging Light Sources and Optical Sensors: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;23(1):247. doi: 10.3390/s23010247. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou N., Li J., Wang S., Zhuang X., Ni S., Luan F., Wu X., Yu S. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Gold and Bismuth Bimetallic Nanoparticles Decorated L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Sensitive Detection of Iron Ions in Water Samples. Nanomaterials. 2021;11:2386. doi: 10.3390/nano11092386. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meng X., Fujita K., Moriguchi Y., Zong Y., Tanaka K. Metal-Dielectric Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Advanced Plasmonic Architectures Towards Multiple Control of Random Lasers. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013;1:573–580. doi: 10.1002/adom.201300153. - DOI
-
- Shi X., Wang Y., Wang Z., Sun Y., Liu D., Zhang Y., Li Q., Shi J. High performance plasmonic random laser based on nanogaps in bimetallic porous nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013;103:23504. doi: 10.1063/1.4813558. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

