Influence of Parameters on the Death Pathway of Gastric Cells Induced by Gold Nanosphere Mediated Phototherapy
- PMID: 35214976
- PMCID: PMC8878397
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12040646
Influence of Parameters on the Death Pathway of Gastric Cells Induced by Gold Nanosphere Mediated Phototherapy
Abstract
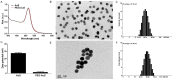
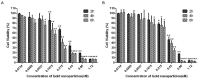
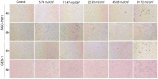
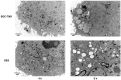
Gold nanosphere (AuS) is a nanosized particle with inert, biocompatible, easily modified surface functionalization and adequate cell penetration ability. Photothermal, photochemical, and vapor effects of AuS could be activated by irradiating with nanosecond laser to cause cell death. Hence, AuS-mediated phototherapy irradiated with nanosecond laser is a promising and minimally-invasive treatment method for cancer therapy. However, various effects require different parameters to be activated. At present, few studies have reported on the influence of parameters of AuS inducing cell death under nanosecond laser irradiation. This makes it very challenging to optimize gold-nanoparticle-mediated specific or synergistic anti-cancer therapy. In this study, we revealed the main parameters and threshold values for AuS-mediated gastric cancer phototherapy with nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation, evaluated the pathway of induced cell death, and discussed the roles of photothermal, photochemical and vapor effects which can induce the cell death. The results showed that AuS-mediated phototherapy activated with nanosecond pulsed laser is an effective method for gastric therapy, mainly based on the photochemical effect. Prolonging the incubation time could decrease the irradiation dose, increase ROS-mediated photothermal effect and vapor effect, and then quickly induce cell death to improve security.
Keywords: gold nanosphere-mediated phototherapy; nanosecond laser; photochemical effect; photothermal effect; vapor effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Brown S.D., Nativo P., Smith J.A., Stirling D., Edwards P.R., Venugopal B., Flint D.J., Plumb J.A., Graham D., Wheate N.J. Gold Nanoparticles for the Improved Anticancer Drug Delivery of the Active Component of Oxaliplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:4678–4684. doi: 10.1021/ja908117a. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

