Computational Indicator Approach for Assessment of Nanotoxicity of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials
- PMID: 35214977
- PMCID: PMC8879952
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12040650
Computational Indicator Approach for Assessment of Nanotoxicity of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials
Abstract
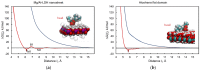
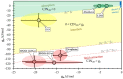
The increasing growth in the development of various novel nanomaterials and their biomedical applications has drawn increasing attention to their biological safety and potential health impact. The most commonly used methods for nanomaterial toxicity assessment are based on laboratory experiments. In recent years, with the aid of computer modeling and data science, several in silico methods for the cytotoxicity prediction of nanomaterials have been developed. An affordable, cost-effective numerical modeling approach thus can reduce the need for in vitro and in vivo testing and predict the properties of designed or developed nanomaterials. We propose here a new in silico method for rapid cytotoxicity assessment of two-dimensional nanomaterials of arbitrary chemical composition by using free energy analysis and molecular dynamics simulations, which can be expressed by a computational indicator of nanotoxicity (CIN2D). We applied this approach to five well-known two-dimensional nanomaterials promising for biomedical applications: graphene, graphene oxide, layered double hydroxide, aloohene, and hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets. The results corroborate the available laboratory biosafety data for these nanomaterials, supporting the applicability of the developed method for predictive nanotoxicity assessment of two-dimensional nanomaterials.
Keywords: cytotoxicity prediction; in silico models; lipid extraction; membrane disruption; two-dimensional nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mikhaylov G., Mikac U., Magaeva A.A., Itin V.I., Naiden E.P., Psakhye I., Babes L., Reinheckel T., Peters C., Zeiser R., et al. Ferri-liposomes as an MRI-visible drug-delivery system for targeting tumours and their microenvironment. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011;6:594–602. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.112. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

