Combined Antagonism of 5-HT2 and NMDA Receptors Reduces the Aggression of Monoamine Oxidase a Knockout Mice
- PMID: 35215325
- PMCID: PMC8875523
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15020213
Combined Antagonism of 5-HT2 and NMDA Receptors Reduces the Aggression of Monoamine Oxidase a Knockout Mice
Abstract
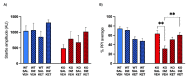
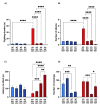
The enzyme monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) catalyzes the degradation of several neurotransmitters, including serotonin. A large body of evidence has shown that genetic MAOA deficiency predisposes humans and mice to aggression and antisocial behavior. We previously documented that the aggression of male MAOA-deficient mice is contributed by serotonin 5-HT2 and glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in the prefrontal cortex (PFC). Indeed, blocking either receptor reduces the aggression of MAOA knockout (KO) mice; however, 5-HT2 receptor antagonists, such as ketanserin (KET), reduce locomotor activity, while NMDA receptor blockers are typically associated with psychotomimetic properties. To verify whether NMDA receptor blockers induce psychotomimetic effects in MAOA KO mice, here we tested the effects of these compounds on prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle reflex. We found that male MAOA KO mice are hypersensitive to the PPI-disrupting properties of NMDA receptor antagonists, including the non-competitive antagonist dizocilpine (DIZ; 0.1, 0.3 mg/kg, IP) and the NR2B subunit-specific blocker Ro-256981 (5, 10 mg/kg, IP). Since KET has been previously shown to counter the PPI deficits caused by NMDA receptor antagonists, we tested the behavioral effects of the combination of KET (2 mg/kg, IP) and these drugs. Our results show that the combination of KET and DIZ potently reduces aggression in MAOA KO mice without any PPI deficits and sedative effects. While the PPI-ameliorative properties of KET were also observed after infusion in the medial PFC (0.05 μg/side), KET did not counter the PPI-disruptive effects of Ro-256981 in MAOA KO mice. Taken together, these results point to the combination of non-subunit-selective NMDA and 5-HT2 receptor antagonists as a potential therapeutic approach for aggression and antisocial behavior with a better safety and tolerability profile than each monotherapy.
Keywords: 5-HT2 receptors; NMDA receptors; aggression; monoamine oxidase A; prepulse inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pharmacological and genetic evidence indicates that combined inhibition of NR2A and NR2B subunit containing NMDA receptors is required to disrupt prepulse inhibition.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Aug;175(1):99-105. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-1785-y. Epub 2004 Feb 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004. PMID: 14985927
-
M100907, a serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist and putative antipsychotic, blocks dizocilpine-induced prepulse inhibition deficits in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Apr;20(4):311-21. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00072-4. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10088132
-
NMDARs mediate the role of monoamine oxidase A in pathological aggression.J Neurosci. 2012 Jun 20;32(25):8574-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0225-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22723698 Free PMC article.
-
The role of monoamine oxidase A in the neurobiology of aggressive, antisocial, and violent behavior: A tale of mice and men.Prog Neurobiol. 2020 Nov;194:101875. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101875. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Prog Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32574581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of monoamine oxidase A in aggression: Current translational developments and future challenges.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Aug 1;69:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26776902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Haloperidol and Olanzapine on Hippocampal Cells' Proliferation in Animal Model of Schizophrenia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7711. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147711. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887056 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor Availability and Its Relationship with Aggression Traits in Healthy Individuals: A Positron Emission Tomography Study with C-11 MDL100907.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 28;24(21):15697. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115697. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958691 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in the orbitofrontal cortex of antisocial individuals.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023 Mar;273(2):411-425. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01480-y. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36094569 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal maternal stress and offspring aggressive behavior: Intergenerational and transgenerational inheritance.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Sep 23;16:977416. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.977416. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36212196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila mutants lacking the glial neurotransmitter-modifying enzyme Ebony exhibit low neurotransmitter levels and altered behavior.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 27;13(1):10411. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36558-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37369755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cherek D.R., Tcheremissine O.V., Lane S.D., Nelson R.J. Psychopharmacology of human aggression: Laboratory and clinical studies. In: Nelson R.J., editor. Biology of Aggression. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2006. pp. 424–446.
-
- Harris A., Lurigio A.J. Mental illness and violence: A brief review of research and assessment strategies. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2007;12:542–551. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2007.02.008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

