Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor, Febuxostat Is Effective against 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Parotid Salivary Gland Injury in Rats Via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Targeting TRPC1/CHOP Signalling Pathway
- PMID: 35215344
- PMCID: PMC8880727
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15020232
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor, Febuxostat Is Effective against 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Parotid Salivary Gland Injury in Rats Via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Targeting TRPC1/CHOP Signalling Pathway
Abstract
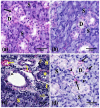
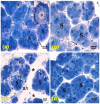
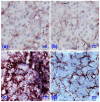
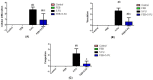
The current research aimed to examine the ameliorative role of febuxostat (FEB), a highly potent xanthine oxidase inhibitor, against 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-induced parotid salivary gland damage in rats, as FEB is a pleiotropic drug that has multiple pharmacological effects. A total of 32 Wistar adult male rats were randomly arranged into four groups. Group 1: the control group; given only the vehicle for 14 days, then given a saline i.p. injection from the 10th to the 14th day. Group 2: the FEB group; rats received FEB (10 mg/kg) once daily po for 14 days before receiving a saline i.p. injection from the 10th to the 14th day. Group 3: the 5-FU group; from the 10th to the 14th day, rats received an intraperitoneal injection of 5-FU (35 mg/kg/day). Group 4: the FEB/5-FU group; rats were pre-treated with FEB po for 14 days before receiving 5-FU i.p injections for five consecutive days from the 10th to the 14th day. Parotid gland damage was detected histologically and biochemically by the evaluation of oxidative stress markers (malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide levels (NOx)), oxidant defences (reduced glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD)), inflammatory markers (tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β)), and transient receptor potential canonical1 (TRCP1) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP). FEB pre-treatment reduced MDA, TNF-, and IL-1 while increasing SOD, GSH, and NOx. FEB also significantly increased TRPC1 and decreased CHOP in parotid gland tissue. In conclusion, FEB pre-treatment reduced 5-FU-induced parotid salivary gland damage not only through its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, but also through its effect on the TRPC1/CHOP signalling pathway.
Keywords: CHOP; TRPC1; febuxostat; fluorouracil; parotid damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bachmeier E., López M.M., Linares J.A., Brunotto M.N., Mazzeo M.A. 5-Fluorouracil and Cyclophosphamide modify functional activity in submandibular gland of rats. J. Oral Res. 2019;8:363–369.
-
- Elmansy M.N., Hegazy E.M. Evaluation of the Apoptotic changes induced by 5-Fluorouracil on the Lingual Mucosa and Salivary glands of male albino rats (Histological, Histomorphometric and Immunohistochemical Study) Egypt. Dent. J. 2020;66:2353–2363. doi: 10.21608/edj.2020.41503.1240. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

