Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty-Acid Supplementation Upregulates Protective Cellular Pathways in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Exhibiting Improvement in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
- PMID: 35215418
- PMCID: PMC8876723
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14040761
Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty-Acid Supplementation Upregulates Protective Cellular Pathways in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Exhibiting Improvement in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have been proposed to improve chronic neuroinflammatory diseases in peripheral and central nervous systems. For instance, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) protects nerve cells from noxious stimuli in vitro and in vivo. Recent reports link PUFA supplementation to improving painful diabetic neuropathy (pDN) symptoms, but cellular mechanisms responsible for this therapeutic effect are not well understood. The objective of this study is to identify distinct cellular pathways elicited by dietary omega-3 PUFA supplementation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) affected by pDN.
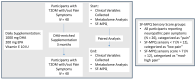
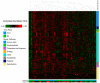
Methods: Forty volunteers diagnosed with type 2 diabetes were enrolled in the "En Balance-PLUS" diabetes education study. The volunteers participated in weekly lifestyle/nutrition education and daily supplementation with 1000 mg DHA and 200 mg eicosapentaenoic acid. The Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire validated clinical determination of baseline and post-intervention pain complaints. Laboratory and untargeted metabolomics analyses were conducted using blood plasma collected at baseline and after three months of participation in the dietary regimen. The metabolomics data were analyzed using random forest, hierarchical clustering, ingenuity pathway analysis, and metabolic pathway mapping.
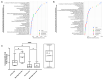
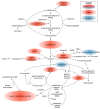
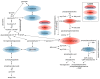
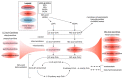
Results: The data show that metabolites involved in oxidative stress and glutathione production shifted significantly to a more anti-inflammatory state post supplementation. Example of these metabolites include cystathionine (+90%), S-methylmethionine (+9%), glycine cysteine-glutathione disulfide (+157%) cysteinylglycine (+19%), glutamate (-11%), glycine (+11%), and arginine (+13.4%). In addition, the levels of phospholipids associated with improved membrane fluidity such as linoleoyl-docosahexaenoyl-glycerol (18:2/22:6) (+253%) were significantly increased. Ingenuity pathway analysis suggested several key bio functions associated with omega-3 PUFA supplementation such as formation of reactive oxygen species (p = 4.38 × 10-4, z-score = -1.96), peroxidation of lipids (p = 2.24 × 10-5, z-score = -1.944), Ca2+ transport (p = 1.55 × 10-4, z-score = -1.969), excitation of neurons (p = 1.07 ×10-4, z-score = -1.091), and concentration of glutathione (p = 3.06 × 10-4, z-score = 1.974).
Conclusion: The reduction of pro-inflammatory and oxidative stress pathways following dietary omega-3 PUFA supplementation is consistent with the promising role of these fatty acids in reducing adverse symptoms associated with neuroinflammatory diseases and painful neuropathy.
Keywords: metabolism; metabolomics; omega-3; painful diabetic neuropathy; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

