Cancer Cell Inhibiting Sea Cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota) Protein as a Novel Anti-Cancer Drug
- PMID: 35215436
- PMCID: PMC8879703
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14040786
Cancer Cell Inhibiting Sea Cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota) Protein as a Novel Anti-Cancer Drug
Abstract
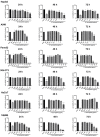
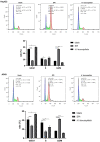
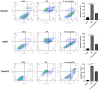
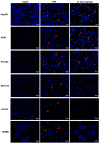
Cancer remains the primary cause of death worldwide. To develop less toxic anti-cancer drugs to relieve the suffering and improve the survival of cancer patients is the major focus in the anti-cancer field. To this end, marine creatures are being extensively studied for their anti-cancer effects, since extracts from at least 10% of the marine organisms have been shown to possess anti-tumor activities. As a classic Chinese traditional medicine, sea cucumbers and compounds extracted from the sea cucumbers, such as polysaccharides and saponins, have recently been shown to exhibit anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant effects. Holothuria leucospilota (H. leucospilota) is a tropical edible sea cucumber species that has been successfully cultivated and farmed in large scales, providing a readily available source of raw materials to support the development of novel marine anti-cancer drugs. However, very few studies have so far been performed on the biological activities of H. leucospilota. In this study, we first investigated the anti-cancer effect of H. leucospilota protein on three cancer cell lines (i.e., HepG2, A549, Panc02) and three normal cell lines (NIH-3T3, HaCaT, 16HBE). Our data showed that H. leucospilota protein decreased the cell viabilities of HepG2, A549, HaCaT, 16HBE in a concentration-dependent manner, while Panc02 and NIH-3T3 in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. We also found that the inhibitory effect of H. leucospilota protein (≥10 μg/mL) on cell viability is near or even superior to EPI, a clinical chemotherapeutic agent. In addition, our data also demonstrated that H. leucospilota protein significantly affected the cell cycle and induced apoptosis in the three cancer cell lines investigated; in comparison, it showed no effects on the normal cell lines (i.e., NIH-3T3, HaCaT and 16HBE). Finally, our results also showed that H. leucospilota protein exhibited the excellent performance in inhibiting cell immigrations. In conclusion, H. leucospilota protein targeted the cancer cell cycles and induced cancer cell apoptosis; its superiority to inhibit cancer cell migration compared with EPI, shows the potential as a promising anti-cancer drug.
Keywords: anti-cancer activity; cell apoptosis; cell migration; marine extractions; sea cucumber protein; targeted effects.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Hu J., Li Y., Li H., Shi F., Xie L., Zhao L., Tang M., Luo X., Jia W., Fan J., et al. Targeting Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1-mediated high oxidative stress suppresses EBV lytic reactivation and sensitizes tumors to radiation therapy. Theranostics. 2020;10:11921–11937. doi: 10.7150/thno.46006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

