Olive Oil Improves While Trans Fatty Acids Further Aggravate the Hypomethylation of LINE-1 Retrotransposon DNA in an Environmental Carcinogen Model
- PMID: 35215560
- PMCID: PMC8878525
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14040908
Olive Oil Improves While Trans Fatty Acids Further Aggravate the Hypomethylation of LINE-1 Retrotransposon DNA in an Environmental Carcinogen Model
Abstract
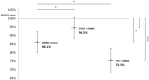
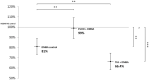
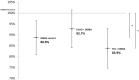
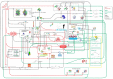
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism that is crucial for mammalian development and genomic stability. Aberrant DNA methylation changes have been detected not only in malignant tumor tissues; the decrease of global DNA methylation levels is also characteristic for aging. The consumption of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) as part of a balanced diet shows preventive effects against age-related diseases and cancer. On the other hand, consuming trans fatty acids (TFA) increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases as well as cancer. The aim of the study was to investigate the LINE-1 retrotransposon (L1-RTP) DNA methylation pattern in liver, kidney, and spleen of mice as a marker of genetic instability. For that, mice were fed with EVOO or TFA and were pretreated with environmental carcinogen 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-a harmful substance known to cause L1-RTP DNA hypomethylation. Our results show that DMBA and its combination with TFA caused significant L1-RTP DNA hypomethylation compared to the control group via inhibition of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) enzymes. EVOO had the opposite effect by significantly decreasing DMBA and DMBA + TFA-induced hypomethylation, thereby counteracting their effects.
Keywords: DMBA; LINE-1 methylation pattern; extra virgin olive oil; trans fatty acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal B.B., Bhardwaj A., Aggarwal R.S., Seeram N.P., Shishodia S., Takada Y. Role of resveratrol in prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:2783–2840. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

