Polymer-Based Wound Dressing Materials Loaded with Bioactive Agents: Potential Materials for the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds
- PMID: 35215637
- PMCID: PMC8874614
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14040724
Polymer-Based Wound Dressing Materials Loaded with Bioactive Agents: Potential Materials for the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds
Abstract
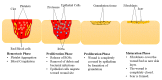
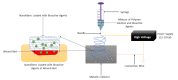
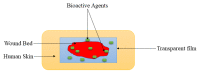
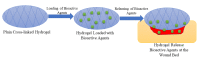
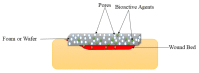
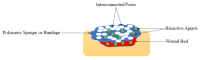
Diabetic wounds are severe injuries that are common in patients that suffer from diabetes. Most of the presently employed wound dressing scaffolds are inappropriate for treating diabetic wounds. Improper treatment of diabetic wounds usually results in amputations. The shortcomings that are related to the currently used wound dressings include poor antimicrobial properties, inability to provide moisture, weak mechanical features, poor biodegradability, and biocompatibility, etc. To overcome the poor mechanical properties, polymer-based wound dressings have been designed from the combination of biopolymers (natural polymers) (e.g., chitosan, alginate, cellulose, chitin, gelatin, etc.) and synthetic polymers (e.g., poly (vinyl alcohol), poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid), polylactide, poly-glycolic acid, polyurethanes, etc.) to produce effective hybrid scaffolds for wound management. The loading of bioactive agents or drugs into polymer-based wound dressings can result in improved therapeutic outcomes such as good antibacterial or antioxidant activity when used in the treatment of diabetic wounds. Based on the outstanding performance of polymer-based wound dressings on diabetic wounds in the pre-clinical experiments, the in vivo and in vitro therapeutic results of the wound dressing materials on the diabetic wound are hereby reviewed.
Keywords: and diabetic foot ulcer; bioactive agents; diabetic wounds; polymers; wound dressings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fabrication of Hybrid Nanofibers from Biopolymers and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly (ε-Caprolactone) for Wound Dressing Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jun 26;13(13):2104. doi: 10.3390/polym13132104. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gelatin-Based Hybrid Scaffolds: Promising Wound Dressings.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;13(17):2959. doi: 10.3390/polym13172959. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34502997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun Nanofibers/Nanofibrous Scaffolds Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles as Effective Antibacterial Wound Dressing Materials.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):964. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070964. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34206857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Polymer-based Wound Dressings for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Overview of State-of-the-art.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(5):527-550. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666170704132523. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28676002 Review.
-
Chitosan/Hyaluronic acid/Alginate and an assorted polymers loaded with honey, plant, and marine compounds for progressive wound healing-Know-how.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Sep 1;186:656-685. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.067. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34271047 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo Evaluation of the Bioactive Nanofibers-Encapsulated Benzalkonium Bromide for Accelerating Wound Repair with MRSA Skin Infection.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Sep 21;17:4419-4432. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S380786. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36172005 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospun Chitosan-Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofiber Dressings Loaded with Bioactive Ursolic Acid Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Aug 25;12(17):2933. doi: 10.3390/nano12172933. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079971 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing of messenger RNA in the healing process of diabetes foot ulcer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 19;15:1468301. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1468301. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39624820 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of biocompatible Zein/Gelatin/Chitosan/PVA based nanofibers loaded with vitamin E-TPGS via dual-opposite electrospinning method.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 11;14(1):23796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74865-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39394234 Free PMC article.
-
Wound dressings incorporating microRNAs: Innovative therapy for diabetic wound treatment.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Sep;25(9):1042-1044. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.67236.14739. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36246066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kakkar R., Madgula K., Nehru Y.V.S., Kakkar J. Polyvinyl alcohol-melamine formaldehyde films and coatings with silver nanoparticles as wound dressings in diabetic foot disease. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2015;4:98–105.
-
- Venault A., Lin K.H., Tang S.H., Dizon G.V., Hsu C.H., Maggay I.V.B., Chang Y. Zwitterionic electrospun PVDF fibrous membranes with a well-controlled hydration for diabetic wound recovery. J. Memb. Sci. 2020;598:117648. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117648. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

