Coagulation System Activation for Targeting of COVID-19: Insights into Anticoagulants, Vaccine-Loaded Nanoparticles, and Hypercoagulability in COVID-19 Vaccines
- PMID: 35215822
- PMCID: PMC8876839
- DOI: 10.3390/v14020228
Coagulation System Activation for Targeting of COVID-19: Insights into Anticoagulants, Vaccine-Loaded Nanoparticles, and Hypercoagulability in COVID-19 Vaccines
Abstract
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), also known as COVID-19, is currently developing into a rapidly disseminating and an overwhelming worldwide pandemic. In severe COVID-19 cases, hypercoagulability and inflammation are two crucial complications responsible for poor prognosis and mortality. In addition, coagulation system activation and inflammation overlap and produce life-threatening complications, including coagulopathy and cytokine storm, which are associated with overproduction of cytokines and activation of the immune system; they might be a lead cause of organ damage. However, patients with severe COVID-19 who received anticoagulant therapy had lower mortality, especially with elevated D-dimer or fibrin degradation products (FDP). In this regard, the discovery of natural products with anticoagulant potential may help mitigate the numerous side effects of the available synthetic drugs. This review sheds light on blood coagulation and its impact on the complication associated with COVID-19. Furthermore, the sources of natural anticoagulants, the role of nanoparticle formulation in this outbreak, and the prevalence of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) after COVID-19 vaccines are also reviewed. These combined data provide many research ideas related to the possibility of using these anticoagulant agents as a treatment to relieve acute symptoms of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccines; hypercoagulability; nanoparticles; natural anticoagulants; targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
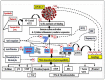
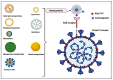
References
-
- Abdellatif A.A.H., Khan R.A., Alhowail A.H., Alqasoumi A., Sajid S.M., Mohammed A.M., Alsharidah M., Al Rugaie O., Mousa A.M. Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021;11:266–283. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2022-0021. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

