Isolation, Characterization, and Molecular Detection of Porcine Sapelovirus
- PMID: 35215935
- PMCID: PMC8877214
- DOI: 10.3390/v14020349
Isolation, Characterization, and Molecular Detection of Porcine Sapelovirus
Abstract
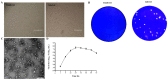
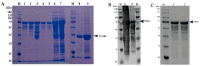
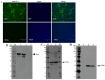
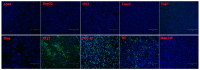
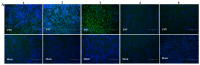
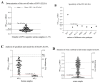
Porcine sapelovirus (PSV) is an important emerging pathogen associated with a wide variety of diseases in swine, including acute diarrhoea, respiratory distress, skin lesions, severe neurological disorders, and reproductive failure. Although PSV is widespread, serological assays for field-based epidemiological studies are not yet available. Here, four PSV strains were recovered from diarrheic piglets, and electron microscopy revealed virus particles with a diameter of ~32 nm. Analysis of the entire genome sequence revealed that the genomes of PSV isolates ranged 7569-7572 nucleotides in length. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the isolated viruses were classified together with strains from China. Additionally, monoclonal antibodies for the recombinant PSV-VP1 protein were developed to specifically detect PSV infection in cells, and we demonstrated that isolated PSVs could only replicate in cells of porcine origin. Using recombinant PSV-VP1 protein as the coating antigen, we developed an indirect ELISA for the first time for the detection of PSV antibodies in serum. A total of 516 swine serum samples were tested, and PSV positive rate was 79.3%. The virus isolates, monoclonal antibodies and indirect ELISA developed would be useful for further understanding the pathophysiology of PSV, developing new diagnostic assays, and investigating the epidemiology of the PSV.
Keywords: ELISA; characterization; isolation; monoclonal antibodies; porcine sapelovirus; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

