Prodynorphin and Proenkephalin in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
- PMID: 35216166
- PMCID: PMC8877714
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23042051
Prodynorphin and Proenkephalin in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Abstract
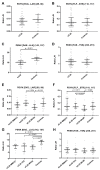
Proenkephalin (PENK) and prodynorphin (PDYN) are endogenous opioid peptides mainly produced in the striatum and, to a lesser extent, in the cerebral cortex. Dysregulated metabolism and altered cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of PENK and PDYN have been described in several neurodegenerative diseases. However, no study to date investigated these peptides in the CSF of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD). Using liquid chromatography-multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry, we evaluated the CSF PDYN- and PENK-derived peptide levels in 25 controls and 63 patients with sCJD belonging to the most prevalent molecular subtypes (MM(V)1, VV2 and MV2K). One of the PENK-derived peptides was significantly decreased in each sCJD subtype compared to the controls without a difference among subtypes. Conversely, PDYN-derived peptides were selectively decreased in the CSF of sCJD MV2K, a subtype with a more widespread overall pathology compared to the sCJD MM(V)1 and the VV2 subtypes, which we confirmed by semiquantitative analysis of cortical and striatal neuronal loss and astrocytosis. In sCJD CSF PENK and PDYN were associated with CSF biomarkers of neurodegeneration but not with clinical variables and showed a poor diagnostic performance. CSF PDYN and PENK-derived peptides had no significant diagnostic and prognostic values in sCJD; however, the distinct marker levels between molecular subtypes might help to better understand the basis of phenotypic heterogeneity determined by divergent neuronal targeting.
Keywords: Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease; biomarkers; mass spectrometry; opioid peptides; prion disease; prodynorphin; proenkephalin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Parchi P., Giese A., Capellari S., Brown P., Schulz-Schaeffer W., Windl O., Zerr I., Budka H., Kopp N., Piccardo P., et al. Classification of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Based on Molecular and Phenotypic Analysis of 300 Subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999;46:224–233. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(199908)46:2<224::AID-ANA12>3.0.CO;2-W. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abu-Rumeileh S., Steinacker P., Polischi B., Mammana A., Bartoletti-Stella A., Oeckl P., Baiardi S., Zenesini C., Huss A., Cortelli P., et al. CSF biomarkers of neuroinflammation in distinct forms and subtypes of neurodegenerative dementia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019;12:2. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0562-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

