The Value of Whole-Genome Sequencing for Mitochondrial DNA Population Studies: Strategies and Criteria for Extracting High-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes
- PMID: 35216360
- PMCID: PMC8876724
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23042244
The Value of Whole-Genome Sequencing for Mitochondrial DNA Population Studies: Strategies and Criteria for Extracting High-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes
Abstract
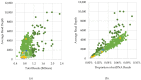
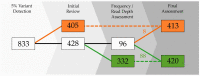
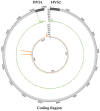
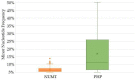
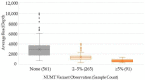
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data present a readily available resource for mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) haplotypes that can be utilized for genetics research including population studies. However, the reconstruction of the mitogenome is complicated by nuclear mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) segments (NUMTs) that co-align with the mtDNA sequences and mimic authentic heteroplasmy. Two minimum variant detection thresholds, 5% and 10%, were assessed for the ability to produce authentic mitogenome haplotypes from a previously generated WGS dataset. Variants associated with NUMTs were detected in the mtDNA alignments for 91 of 917 (~8%) Swedish samples when the 5% frequency threshold was applied. The 413 observed NUMT variants were predominantly detected in two regions (nps 12,612-13,105 and 16,390-16,527), which were consistent with previously documented NUMTs. The number of NUMT variants was reduced by ~97% (400) using a 10% frequency threshold. Furthermore, the 5% frequency data were inconsistent with a platinum-quality mitogenome dataset with respect to observed heteroplasmy. These analyses illustrate that a 10% variant detection threshold may be necessary to ensure the generation of reliable mitogenome haplotypes from WGS data resources.
Keywords: NUMTs; heteroplasmy; massively parallel sequencing; mitochondrial DNA; next-generation sequencing; nuclear elements of mtDNA; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome Variation in the Swedish Population.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;14(11):1989. doi: 10.3390/genes14111989. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002932 Free PMC article.
-
Platinum-Quality Mitogenome Haplotypes from United States Populations.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 29;11(11):1290. doi: 10.3390/genes11111290. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33138247 Free PMC article.
-
The Mighty NUMT: Mitochondrial DNA Flexing Its Code in the Nuclear Genome.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 27;13(5):753. doi: 10.3390/biom13050753. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinguishing mitochondrial DNA and NUMT sequences amplified with the precision ID mtDNA whole genome panel.Mitochondrion. 2020 Nov;55:122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Mitochondrion. 2020. PMID: 32949792
-
Sequencing and characterizing human mitochondrial genomes in the biobank-based genomic research paradigm.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jun;68(6):1610-1625. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2736-7. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39843848 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Identification of Mitochondrial Pseudogenes (NUMTs) in the Human Telomere-to-Telomere Reference Genome.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;14(11):2092. doi: 10.3390/genes14112092. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003036 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Mitochondrial DNA Genome Variation in the Swedish Population.Genes (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;14(11):1989. doi: 10.3390/genes14111989. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002932 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and origin of Kazakh Tobet Dogs.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 4;14(1):23137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74061-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39367220 Free PMC article.
-
Helena's Many Daughters: More Mitogenome Diversity behind the Most Common West Eurasian mtDNA Control Region Haplotype in an Extended Italian Population Sample.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6725. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126725. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743173 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

