Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation Accelerate Vascular Calcification in a Model of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
- PMID: 35216422
- PMCID: PMC8878394
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23042302
Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation Accelerate Vascular Calcification in a Model of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
Abstract
Arterial calcification is a common feature of pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), a disease characterized by ABCC6 mutations, inducing a deficiency in pyrophosphate, a key inhibitor of calcium phosphate crystallization in arteries.
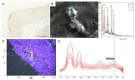
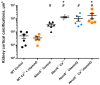
Methods: we analyzed whether long-term exposure of Abcc6-/- mice (a murine model of PXE) to a mild vitamin D supplementation, with or without calcium, would impact the development of vascular calcification. Eight groups of mice (including Abcc6-/- and wild-type) received vitamin D supplementation every 2 weeks, a calcium-enriched diet alone (calcium in drinking water), both vitamin D supplementation and calcium-enriched diet, or a standard diet (controls) for 6 months. Aorta and kidney artery calcification was assessed by 3D-micro-computed tomography, Optical PhotoThermal IR (OPTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and Yasue staining.
Results: at 6 months, although vitamin D and/or calcium did not significantly increase serum calcium levels, vitamin D and calcium supplementation significantly worsened aorta and renal artery calcification in Abcc6-/- mice.
Conclusions: vitamin D and/or calcium supplementation accelerate vascular calcification in a murine model of PXE. These results sound a warning regarding the use of these supplementations in PXE patients and, to a larger extent, patients with low systemic pyrophosphate levels.
Keywords: ABCC6; calcification; calcium; pseudoxanthoma elasticum; pyrophosphate; vascular; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nitschke Y., Baujat G., Botschen U., Wittkampf T., du Moulin M., Stella J., Le Merrer M., Guest G., Lambot K., Tazarourte-Pinturier M.-F., et al. Generalized Arterial Calcification of Infancy and Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Can Be Caused by Mutations in Either ENPP1 or ABCC6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;90:25–39. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bäck M., Aranyi T., Cancela M.L., Carracedo M., Conceição N., Leftheriotis G., Macrae V., Martin L., Nitschke Y., Pasch A., et al. Endogenous Calcification Inhibitors in the Prevention of Vascular Calcification: A Consensus Statement From the COST Action EuroSoftCalcNet. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018;5:196. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

