Platelet-Released Factors: Their Role in Viral Disease and Applications for Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Therapy
- PMID: 35216433
- PMCID: PMC8876984
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23042321
Platelet-Released Factors: Their Role in Viral Disease and Applications for Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Therapy
Abstract
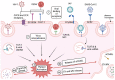
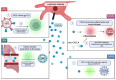
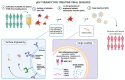
Platelets, which are small anuclear cell fragments, play important roles in thrombosis and hemostasis, but also actively release factors that can both suppress and induce viral infections. Platelet-released factors include sCD40L, microvesicles (MVs), and alpha granules that have the capacity to exert either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory effects depending on the virus. These factors are prime targets for use in extracellular vesicle (EV)-based therapy due to their ability to reduce viral infections and exert anti-inflammatory effects. While there are some studies regarding platelet microvesicle-based (PMV-based) therapy, there is still much to learn about PMVs before such therapy can be used. This review provides the background necessary to understand the roles of platelet-released factors, how these factors might be useful in PMV-based therapy, and a critical discussion of current knowledge of platelets and their role in viral diseases.
Keywords: microparticles; microvesicle; platelets; therapy; vesicles; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Platelet microvesicles in health and disease.Platelets. 2017 May;28(3):214-221. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2016.1265924. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Platelets. 2017. PMID: 28102737 Review.
-
Platelets and extracellular vesicles and their cross talk with cancer.Blood. 2021 Jun 10;137(23):3192-3200. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019004119. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33940593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Vascular Disease Treatment on Platelet-Derived Microvesicles.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017 Dec;31(5-6):627-644. doi: 10.1007/s10557-017-6757-7. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017. PMID: 29164426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1545:177-188. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6728-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27943214
-
Platelet-released extracellular vesicles: the effects of thrombin activation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 14;79(3):190. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04222-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35288766 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Research on Platelet Activity in Health and Disease 3.0.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 16;23(10):5530. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105530. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628340 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Blood Clotting: The Many Roles of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 14;12(8):1850. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081850. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Regenerative Medicine Treatment for Chronic Pain: A Consensus Report from a Multispecialty Working Group.J Pain Res. 2024 Sep 11;17:2951-3001. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S480559. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39282657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of heterologous flavivirus immunity in preventing urban transmission of yellow fever virus.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 10;15(1):9728. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54146-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39523371 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet distribution width as an useful indicator of influenza severity in children.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08890-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38166827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bizzozero G. Sur Un Nouvel Èlèment Morphologique Du Sang Chez Les Mammiferes et Son Importance Dans La Thrombose et Dans La Coagulation. Arch. Ital. Biol. 1882;1:1–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

