Tryptophan Metabolites Regulate Neuropentraxin 1 Expression in Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 35216489
- PMCID: PMC8874566
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23042369
Tryptophan Metabolites Regulate Neuropentraxin 1 Expression in Endothelial Cells
Abstract
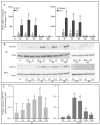
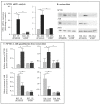
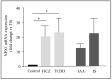
In patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and in animal models of CKD, the transcription factor Aryl Hydrocabon Receptor (AhR) is overactivated. In addition to the canonical AhR targets constituting the AhR signature, numerous other genes are regulated by this factor. We identified neuronal pentraxin 1 (NPTX1) as a new AhR target. Belonging to the inflammatory protein family, NPTX1 seems of prime interest regarding the inflammatory state observed in CKD. Endothelial cells were exposed to tryptophan-derived toxins, indoxyl sulfate (IS) and indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). The adenine mouse model of CKD was used to analyze NPTX1 expression in the burden of uremia. NPTX1 expression was quantified by RT-PCR and western blot. AhR involvement was analyzed using silencing RNA. We found that IS and IAA upregulated NPTX1 expression in an AhR-dependent way. Furthermore, this effect was not restricted to uremic indolic toxins since the dioxin 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and the tryptophan photoproduct 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) do the same. In CKD mice, NPTX1 expression was increased in the aorta. Therefore, NPTX1 is a new target of AhR and further work is necessary to elucidate its exact role during CKD.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; indole-3-acetic acid; indolic uremic toxins; indoxyl sulfate; neuropentraxin 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- European Uremix Toxins Work Group. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.uremic-toxins.org.
-
- Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium. Matsushita K., van der Velde M., Astor B.C., Woodward M., Levey A., de Jong P.E., Coresh J., Gsevoort R.T. Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:2073–2081. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

