Neuronal mitochondria transport Pink1 mRNA via synaptojanin 2 to support local mitophagy
- PMID: 35216662
- PMCID: PMC9081165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.035
Neuronal mitochondria transport Pink1 mRNA via synaptojanin 2 to support local mitophagy
Abstract
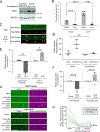
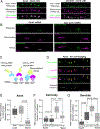
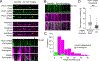
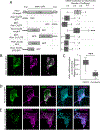
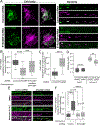
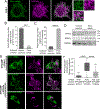
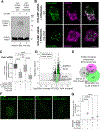
PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) is a short-lived protein required for the removal of damaged mitochondria through Parkin translocation and mitophagy. Because the short half-life of PINK1 limits its ability to be trafficked into neurites, local translation is required for this mitophagy pathway to be active far from the soma. The Pink1 transcript is associated and cotransported with neuronal mitochondria. In concert with translation, the mitochondrial outer membrane proteins synaptojanin 2 binding protein (SYNJ2BP) and synaptojanin 2 (SYNJ2) are required for tethering Pink1 mRNA to mitochondria via an RNA-binding domain in SYNJ2. This neuron-specific adaptation for the local translation of PINK1 provides distal mitochondria with a continuous supply of PINK1 for the activation of mitophagy.
Keywords: OMP25; PINK1; Parkinson disease; RNA transport; SYNJ2BP; hitchhiking; local translation; mitophagy; synaptojanin2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Z.H. is a co-founder of Rugen Therapeutics and Myro Therapeutics. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hitchhiker's guide through the axon: transport and local translation of Pink1 mRNA support axonal mitophagy.Autophagy. 2022 May;18(5):947-948. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2071081. Epub 2022 May 9. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35532369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biever A, Glock C, Tushev G, Ciirdaeva E, Dalmay T, Langer JD, and Schuman EM (2020). Monosomes actively translate synaptic mRNAs in neuronal processes. Science 367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

